Designed for digital marketers, SEO professionals, and business owners, our “SEO 2.0: How to Win with Integrated SEO & Omni-Channel Search Everywhere Optimisation” white paper has been created for those who need to understand how the search landscape has changed and what strategies are required to succeed in 2026 and the years ahead.
Created by our very own SEO agency with decades of combined experience added into the mx, you’ll be introduced to our new SEO 2.0 Framework, which provides a holistic model for achieving visibility across all discovery platforms. From traditional search engines to AI answer engines, LLMs (ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity), social media platforms, Q&A communities (Quora and Reddit), and community forums, we’ll explain what modern search discovery means, backed by extensive research, official data, and real-world examples.

SEO 2.0 – Integrated SEO and Search Everywhere Optimisation
Editor’s Note [22.12.25]: This white paper represents a significant refresh of our original article titled, “The Integrated Approach to SEO and Digital Marketing,” first published on 11 June 2015 and last updated on 7 October 2024. What began as a foundational guide to integrated digital marketing has been completely reimagined for the AI world we now live in. This 2025 update expands the original concepts of branding, content creation, SEO, and social media integration into a full SEO 2.0 framework that addresses the fragmented discovery ecosystem we now operate in. New sections include AI Overviews, LLM-based search engines, the transformation of SERP real estate, Search Everywhere Optimisation, and a comprehensive glossary of emerging terminology including GEO, AEO, AIO, and LLMO.
What is Digital Marketing & How Does it Relate to SEO?
- 1 What is Digital Marketing & How Does it Relate to SEO?
- 2 Is SEO Dead?
-
3
The New SERP: Understanding the Changes in Google’s Real Estate
- 3.1 The Dominance of AI Overviews (Formerly SGE)
- 3.2 People Also Ask (PAA) & Featured Snippets
- 3.3 The Local Pack & Map-Based Results
- 3.4 Shopping Results, Product Carousels & Merchant Feeds
- 3.5 Shopping Ads (Product Listing Ads)
- 3.6 Product Carousels & Knowledge Panels
- 3.7 The Importance of Product Feeds
- 3.8 Media: The Integration of Video, Image & News Carousels
- 3.9 Video Carousels (YouTube)
- 3.10 Image Packs
- 3.11 Top Stories (News Carousel)
-
4
Where Discovery Happens Now: The Omni-Channel Search Ecosystem
- 4.1 Traditional Search Engines like Google & Bing
- 4.2 Google’s AI Initiatives: A Closer Look
- 4.3 AI Answer Engines: The Rise of ChatGPT, Perplexity & Gemini
- 4.4 AI Search Market Share (December 2025)
- 4.5 The Value of AI-Referred Traffic
- 4.6 Social Discovery: Why YouTube & TikTok are the New Search Bars
- 4.7 TikTok: The Gen Z Search Engine
- 4.8 YouTube: The World’s Second-Largest Search Engine
- 4.9 Social Media Usage Statistics (2025)
- 4.10 Community Platforms: Reddit, Quora & Forums as Discovery Hubs
- 4.11 Reddit: The Front Page of the Internet
- 4.12 Quora & Niche Forums
- 4.13 Top Citation Sources in AI Overviews
-
5
The Overlap: Where Search Engine Algorithms & AI Intersect
- 5.1 The Pre-Generative Era: AI for Ranking & Interpretation (2013-2022)
- 5.2 E-E-A-T as the Foundation for Both Algorithm & AI Trust
- 5.3 How Structured Data (Schema) Feeds Both Search & AI Models
- 5.4 The Role of Schema in Traditional SEO
- 5.5 The Role of Schema in AI SEO
- 5.6 Key Schema Types for AI Visibility
- 5.7 The Role of Citations & Links as Universal Authority Signals
- 5.8 The Expanded Web of Trust
- 5.9 The Data on Rankings & AI Citations
- 6 SEO 2.0: The Integrated SEO & Organic Marketing Framework
- 7 The Four Pillars of SEO 2.0
- 8 Case Study: An SEO 2.0 Audit
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Appendix A: The SEO 2.0 Glossary
- 11 References
Lets start with the basics. Digital marketing, in its purest form, is the promotion of products and services through digital channels. For years, this was understood through the lens of silo’d strategies, where components like branding, content, SEO, paid advertising, and social media worked in isolation.
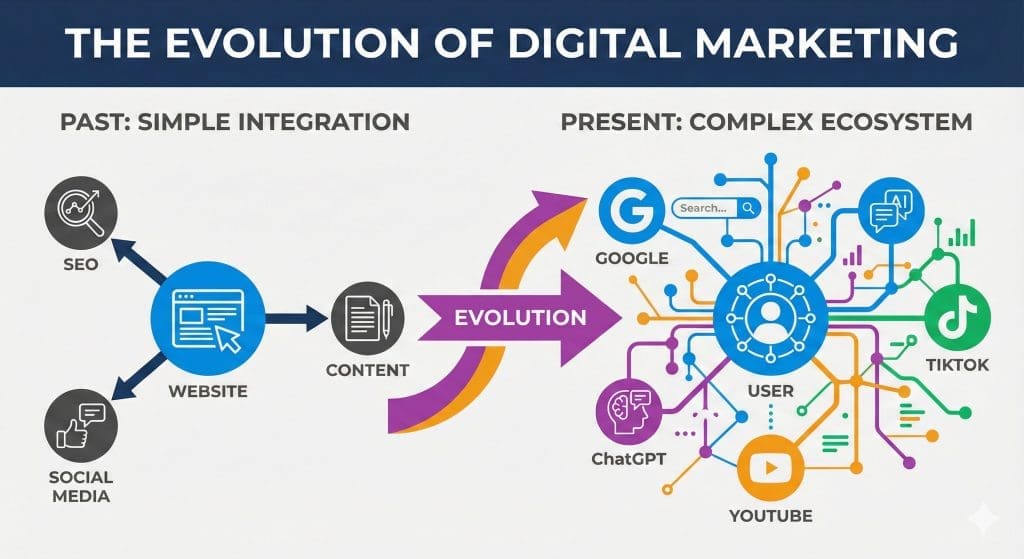
What is digital marketing and the evolution of search
As early as 2015 we identified that this disjointed silo’d approach was ineffective, not just for SEO but digital marketing as a whole. Our goal was to create a seamless user journey, driving traffic from various channels to a high-converting central hub (the website) using an integrated approach to SEO and digital marketing.
What’s changed since 2015 is that the “spider diagram” of marketing, once centered around the the website, has become a complex, multi-dimensional scenario where the user journey is no longer linear. Discovery doesn’t just lead to your website; it happens within walled gardens like TikTok, in the conversational interfaces of LLMs and AI chatbots, and across a fragmented landscape of community platforms. This white paper builds upon our core principles of integrated digital marketing and develops them into a full framework that we call “SEO 2.0”.
Is SEO Dead?
The statement, “SEO is dead,” has been a recurring headline in the digital marketing industry for over a decade. It’s a powerful claim that generates clicks and sparks debate, but it fundamentally misses the point.

Is SEO dead?
As covered in our “Death of SEO” report, the phrase “SEO has died” appeared nearly 5,000 times between 2016 and 2020 alone according to Ahrefs, nearly two full years before the launch of ChatGPT.
AI Means The Death of SEO? Not So Fast – Let’s Look At How AI is Shaping The Future of SEO
Today, a simple Google search for the term yields tens of thousands of results, illustrating a persistent anxiety about the future of SEO.
This section tackles the debate head-on. We will explore the compelling data that fuels the “death of SEO” narrative before providing a clear and evidence-based rebuttal that SEO isn’t dead; instead the concept of ‘search’ is something far more complex, strategic, and integrated where the need for optimisation has never been more critical.
The Argument for the “Death of SEO”
The anxiety surrounding SEO isn’t surprising. We’ve seen fractured seismic shifts in technology and user behaviour, leading to a quantifiable erosion of the traditional search model, which has led to questions like below:
“With AI-generated results taking centre stage, will the standard ten blue links (organic search results), which have already been demoted below sponsored results, local results, ‘people also ask’ results, and so on, be pushed out of existence?”
The primary evidence supporting this concern can be grouped into several main categories.
The Decline of Traditional Search Engine Volume
The most significant macro-trend is the projected decline in the use of traditional search engines as the primary gateway to the internet.
Authoritative research from Gartner predicts that by 2026, traditional search engine volume will decrease by a staggering 25% as users increasingly turn to AI chatbots and other virtual agents for answers.
This isn’t a distant forecast; it’s a near-term reality that demands immediate strategic attention and the implications of this shift are profound. For over two decades, Google has been the de facto starting point for the internet. Businesses have built entire marketing strategies around the assumption that if they could rank on Google, they could reach their customers. That assumption is now being challenged at a fundamental level.
The Rise of the Zero-Click SERP
Even when users do turn to Google, their behaviour has fundamentally changed.
The SERP is no longer a simple list of links; it is a complex and ever-changing answer engine in itself. The proliferation of features like AI Overviews, Featured Snippets, and “People Also Ask” boxes means that users can often get the information they need without ever clicking through to a website. This phenomenon, known as “zero-click search” has a direct and severe impact on organic traffic.
| Impact Area | Key Statistic | Implication |
| AI Overview Impact (Not Cited) | Organic CTR plummets by 65.2% year-over-year | Failure to be cited in an AI Overview is tantamount to being invisible. |
| AI Overview Impact (Cited) | Brands earn 35% higher organic CTR and 91% higher paid CTR | Being cited in AI Overviews provides a significant competitive advantage. |
| Zero-Click Searches (Mobile) | Over 60% of mobile Google searches end without a click | Optimising for rankings alone is a failing strategy. |
| Publisher Impact | One publisher reported an 89% drop in CTR | The economic model for content creators is under direct threat. |
| AI Traffic Conversion | AI search traffic converts at 5x the rate of traditional organic (14.2% vs 2.8%) | The traffic that does come through from AI is exceptionally valuable. |
These data points create a compelling case that the old model of SEO focused primarily on achieving a high rank in the “10 blue links” is indeed dying. Relying on this single channel for visibility and traffic is no longer a sustainable strategy.
AI-Generated Content & Misinformation
The rise of generative AI has created another challenge: a flood of AI-generated content that is polluting search results.
As our “Death of SEO” article notes, the amount of AI-generated and fake content that has flooded Google since the introduction of generative AI in 2022 has been unprecedented. This has led to a wave of misinformation, SEO spam, and deceptive search results that often prioritise engagement over accuracy.
The result has been an erosion of user trust in search results. Users are now often met with AI-fabricated articles, fake images, and misleading summaries, making it harder than ever to distinguish fact from fiction. This environment makes the principles of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) more important than ever, as both users and algorithms seek out genuinely reliable sources.
The Rebuttal: SEO is More Alive Than Ever
The argument that SEO is dead is a fallacy based on a narrow and outdated definition of the term. SEO has not disappeared; it is simply that the concept of search has taken on a whole new meaning.
The fundamental principles of SEO remain unchanged and are, in fact, more important than ever:
- Understanding User Intent: Identifying what a user truly wants when they type a query.
- Creating Value: Delivering the most accurate, comprehensive, and helpful content to satisfy that intent.
- Establishing Authority: Proving to both users and algorithms that you are a trustworthy source of information.
What has changed is the “where”, and to a lesser degree, the “how”.
The playing field has expanded from a single stadium (Google) to a vast, interconnected ecosystem of discovery platforms. The user journey is no longer linear. A query that once started on Google might now begin on YouTube, be refined in ChatGPT, and end with a purchase based on a recommendation in a Reddit forum.
The Omni-Channel Imperative or Search Everywhere Optimisation
For most of us, this means an omni-channel approach or form of integrated digital marketing isn’t just the future, it’s a necessity right now.
The practice of optimisation must evolve from Search Engine Optimisation to Search Everywhere Optimisation.
This is the foundation of our integrated SEO philosophy. It’s a recognition that your audience is distributed and your strategy must be too. SEO is no longer just about Google. It’s about being the answer, everywhere.
For a complete guide to SEO terms and the many different names used to describe search optimisation techniques in 2026, see below:
From SEO to GEO: The Ultimate AI SEO Guide (AI Mode, AI Overviews, RAG, AIO, AEO & LLM SEO)
The AGI Caveat
It is worth acknowledging the most extreme version of the “death of SEO” argument, which centres on the potential development of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). If this were to happen, true AGI would have the ability to learn in real-time, crawl the web, and update its own knowledge base continuously. In such a scenario, the need for a traditional search engine index, and by extension SEO, could theoretically disappear.
However, this remains a speculative future.
The current generation of AI tools, including ChatGPT and Google Gemini, are not AGI. They rely on training data, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) from web indexes, and partnerships with search engines. For the foreseeable future, the principles of creating discoverable, authoritative, and well-structured content will remain the key to visibility.
The real conversation should be around adaptation. The businesses that will win in this new era are those that embrace the complexity, understand the new user journey, and invest in a truly integrated strategy that ensures their brand is visible at every possible point of discovery.
The New SERP: Understanding the Changes in Google’s Real Estate
The Google Search Engine Results Page (SERP) of today is barely recognisable from the simple, ordered list of a few years ago.
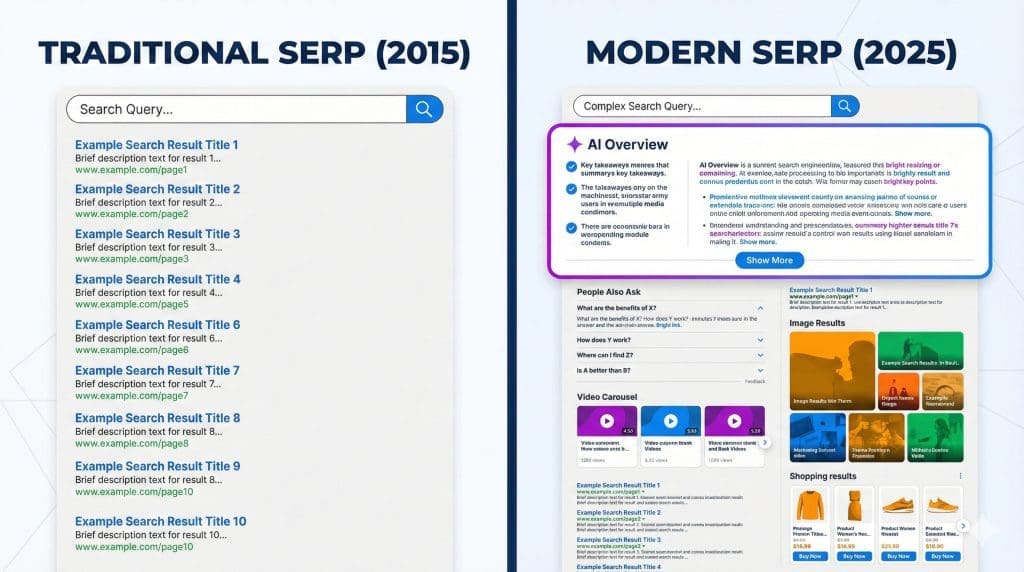
Old-school SERP vs the new SERP
The prime “real estate” that was once dominated by ten organic blue links has been systematically carved up, redeveloped, and repopulated by a host of dynamic features that change based on search intent. These features are designed to provide answers directly on the SERP, often removing the need for a user to click through to a website at all.
For businesses and marketers, understanding this new landscape is a fundamental requirement for survival.
The Dominance of AI Overviews (Formerly SGE)
At the top of the new SERP hierarchy sits the AI Overview. This feature, which evolved from Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) experiment, provides a synthesised, narrative answer to a user’s query by combining information from multiple web sources. It is the most significant change to the SERP in over a decade.
From SGE to AI Overviews
The switch to AI Overviews began in May 2023 when Google introduced the Search Generative Experience (SGE) as an experimental feature in Google Labs.
This marked Google’s first public foray into generative AI within its primary search interface. By May 2024, Google officially rebranded SGE as “AI Overviews,” making it a more integrated and widely available feature.
As of December 2025, Google announced that AI Mode, powered by Gemini 3 Flash, is now the global default for AI-enhanced search experiences
Key Statistics on AI Overviews
| Metric | Statistic |
| Global Prevalence | AI Overviews appear in approximately 18% of all global Google searches |
| Informational Queries | Appear in over 30% of informational queries |
| Long-Tail Queries | Queries with 8+ words have a 57% chance of triggering AI Overviews |
| User Reach | Used by more than 1 billion people globally |
| Usage Increase | AI Overviews drive a 10%+ increase in queries for search types that show them |
The Impact on Visibility
The impact of AI Overviews is twofold:
- For brands cited within the overview, it provides an unparalleled level of authority and visibility, acting as a powerful endorsement that can drive higher-quality clicks.
- For those not cited, it creates a significant barrier, pushing their organic listings further down the page and drastically reducing the likelihood of a click.
This creates a “winner-take-all” dynamic where being cited is essential.
People Also Ask (PAA) & Featured Snippets
Before AI Overviews, Featured Snippets and PAA boxes were the original and primary drivers of the zero-click search phenomenon. They still remain critical components of the modern SERP and are often the source of information for AI Overviews themselves.
Featured Snippets
Featured Snippets are boxes that provide a direct, concise answer to a query, extracted from a single web page.
They often appear for question-based searches (e.g. “what is integrated SEO?”) and can take several forms:
- Paragraph Snippets: A block of text, typically 40-60 words, that directly answers the query.
- List Snippets: A bulleted or numbered list, often used for “how-to” or “best of” queries.
- Table Snippets: A table of data, often used for comparisons or specifications.
People Also Ask (PAA)
PAA boxes are accordion-style boxes that present a list of related questions to the user’s original query. Clicking on a question reveals a short, snippet-style answer, again extracted from a web page.
PAA boxes are a powerful tool for understanding user intent and identifying related topics for content creation. They also represent a significant opportunity for visibility, as each question answered is a chance to capture a user’s attention.
The Local Pack & Map-Based Results
For any query with local intent, the Local Pack is one of the most prominent features on the SERP. It typically displays a map and a list of three local businesses, along with their contact information, reviews, and a link to their website.
When the Local Pack Appears
The Local Pack is triggered by queries that include a geographic modifier (e.g. “plumbing supplies Birmingham”) or by queries where Google infers local intent based on the user’s location (e.g. “plumbing supplies near me” or even just “plumbing supplies”.
For local businesses, ranking in the Local Pack is often more important than ranking in the traditional organic results, as they are typically featured high on the page and capture users with high purchase intent.
Key Ranking Factors for the Local Pack
Ranking in the Local Pack is determined by a different set of factors than traditional organic SEO.
Key factors include:
- Google Business Profile (GBP) Optimisation: A complete and accurate GBP is essential.
- Relevance: How well the business matches the user’s query.
- Distance: The proximity of the business to the user’s location.
- Prominence: The overall online reputation of the business, including reviews, citations, and links.
Shopping Results, Product Carousels & Merchant Feeds
For transactional and commercial queries, the SERP transforms into a rich, visual shopping experience. This is driven by Google’s Merchant Center feed and includes several distinct features.
Shopping Ads (Product Listing Ads)
These are visually-driven ads that display a product image, price, and store name at the very top of the SERP. They are highly effective for capturing users with immediate purchase intent.
Product Carousels & Knowledge Panels
For product-specific queries, Google often displays a Knowledge Panel with detailed product information, including specifications, reviews, and price comparisons from multiple retailers. Scrollable product carousels can also appear within the organic results.
The Importance of Product Feeds
To appear in Shopping results, businesses must submit a product feed to Google Merchant Center. This feed contains detailed information about each product, including title, description, price, availability, and images. Optimising this feed is a critical component of e-commerce SEO.
Media: The Integration of Video, Image & News Carousels
Google’s algorithm is increasingly multimodal, recognising that a text-based link is not always the best answer to a query. As a result, the SERP is now heavily populated with content from other Google properties and media types.
Video Carousels (YouTube)
A significant portion of SERPs now include a carousel of videos, almost exclusively from YouTube. For “how-to” queries, product reviews, and many informational searches, video is often the preferred format. This makes YouTube SEO a critical component of any comprehensive search strategy.
Image Packs
For queries where visual information is important (e.g., “kitchen design ideas,” “fence panel styles”), Google displays a block of images from Google Images. Optimising images with descriptive filenames, ALT text, and surrounding context is essential for capturing this traffic.
Top Stories (News Carousel)
For newsworthy topics, a carousel of articles from Google News-approved publishers appears at the top of the SERP. For brands that produce timely, newsworthy content, this is a valuable source of visibility.
The reality is that the “10 blue links” are no longer the primary focus. Visibility now depends on a brand’s ability to appear within these various features. This requires a multi-faceted strategy that goes beyond traditional on-page optimisation and embraces structured data, answering questions, local SEO, video content, and a deep understanding of how to become a citable source for Google’s AI.
Where Discovery Happens Now: The Omni-Channel Search Ecosystem
Success in 2026 requires a fundamental shift in mindset where we must stop thinking about “search” as a single destination and start seeing it as a distributed ecosystem.
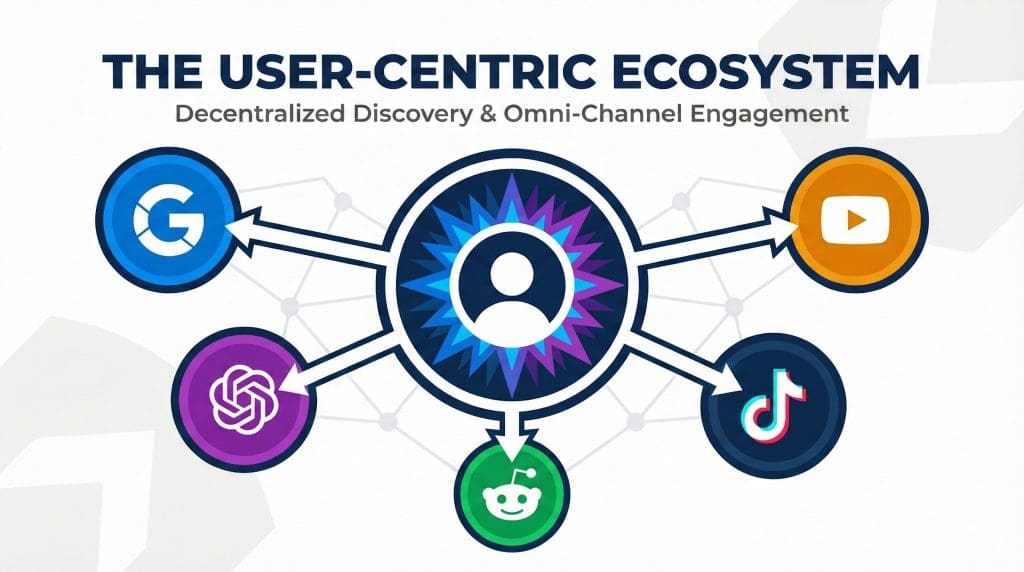
User-centric, omni-channel search discovery
Your customers are no longer starting their journey in one predictable place. They are asking questions, discovering products, and forming opinions across a wide array of platforms, each with its own rules of engagement and algorithms for discovery.
Traditional Search Engines like Google & Bing
Despite the fragmentation, traditional search engines remain a dominant force.
Google still processes the vast majority of global search queries and is the starting point for many user journeys. According to Statcounter, Google holds over 90% of the global search engine market share. However, its role has clearly changed from a directory of websites to an answer engine in its own right.
Google’s AI Initiatives: A Closer Look
Understanding Google’s various AI initiatives is crucial for modern SEO. The terminology can be confusing, so here is a clarification:
| Feature | Description | Status |
| SGE (Search Generative Experience) | Google’s earlier Search Labs experiment name for generative AI in Search (announced May 2023). | Predecessor to AI Overviews |
| AI Overviews | AI-generated summaries that appear inside Google Search for some queries. | Live, appearing in ~18% of global searches |
| AI Mode | A more complete “AI search mode” for handling complex questions with follow-ups. Uses query fan-out technique. | Rolled out broadly in US by May 2025, 100M+ monthly active users |
| Deep Search | A deeper research mode inside AI Mode that can issue hundreds of searches and generate a fully-cited report. | Announced at Google I/O 2025 |
Optimisation for Google and Bing is still critical, but the strategy must now focus on visibility within their rich features (AI Overviews, Local Packs, etc.) rather than just the organic blue links.
AI Answer Engines: The Rise of ChatGPT, Perplexity & Gemini
This is the most disruptive new category in the discovery ecosystem. Platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s own Gemini are becoming the first port of call for users seeking complex answers and synthesised information. The data on their growth is staggering.
| Platform | Market Share | Key Statistics | Strategic Importance |
| ChatGPT | 61.3% | 800M weekly active users; 5.8B monthly visits; 81% AI chatbot market share | The market leader, shaping user expectations for conversational AI. Being cited here establishes broad authority. |
| Microsoft Copilot | 14.1% | 33M active users globally | Integrated into the Bing and Microsoft enterprise ecosystems, crucial for B2B and professional visibility. |
| Google Gemini | 13.4% | 2B monthly users globally; powers AI Overviews reaching 1B+ users | Directly powers Google’s AI Overviews, giving it massive reach. Success here is directly tied to Google SERP visibility. |
| Perplexity | 6.4% | 22M+ monthly active users; 30% of users in senior leadership roles | Known for its focus on accuracy and rigorous citation, making it a key target for establishing factual, data-driven authority. |
The Value of AI-Referred Traffic
While the narrative of declining clicks can seem bleak, the data reveals a powerful counter-narrative where traffic that originates from AI search can be exceptionally valuable.
An analysis of over 12 million website visits found that AI search traffic converts at 5 times the rate of traditional organic traffic (14.2% vs. 2.8%). This dramatic difference is attributed to user intent.
A user arriving from an AI-generated answer has already had their initial, informational queries satisfied. They are further along in their decision-making journey, more educated on the topic, and clicking through for validation or to take a specific action.
Optimising for these platforms is a a practice known as Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO) or LLM Optimisation (LLMO), which requires a different approach. It’s less about keywords and more about creating clear, well-structured, and highly authoritative content that is easy for AI models to parse, trust, and cite.
For a significant and growing segment of the population, particularly younger demographics, social media platforms are the primary search engines. This is especially true for discovery, inspiration, and product research.
TikTok: The Gen Z Search Engine
A staggering 40% of Gen Z now prefer using TikTok over Google for search . This statistic, which originated from Google’s own internal research, sent shockwaves through the industry. TikTok’s algorithm excels at surfacing relevant content based on user interests, making it a powerful engine for discovery, particularly for topics like restaurants, travel, fashion, and product recommendations.
YouTube: The World’s Second-Largest Search Engine
YouTube is the world’s second-largest search engine. According to Pew Research Center, 84% of U.S. adults use YouTube, and 90% of Gen Z are regular users. It is the go-to platform for “how-to” content, product reviews, and visual explanations. If you are not creating video content, you are invisible to a huge portion of your potential audience.
| Platform | U.S. Adult Usage | Key Demographic | Primary Use Case |
| YouTube | 84% | All demographics | How-to, reviews, entertainment |
| 68% | Older demographics | Community, news, local | |
| 51% | Younger demographics | Visual discovery, shopping | |
| TikTok | 37% (up from 21% in 2021) | Gen Z, Millennials | Discovery, entertainment, search |
| 30% | Professionals | B2B, career, industry news |
Optimisation on these platforms (Social Media Optimisation) involves understanding their unique algorithms, using relevant hashtags, creating engaging and shareable content, and leveraging their native analytics to understand what resonates with your audience.
Community Platforms: Reddit, Quora & Forums as Discovery Hubs
When users want authentic, real-world opinions and niche expertise, they turn to community platforms. These are the digital campfires where genuine conversations happen, and they are a goldmine of user intent data.
Reddit: The Front Page of the Internet
Often called “the front page of the internet,” Reddit is a collection of thousands of niche communities (subreddits). It is a primary source for product recommendations, troubleshooting advice, and unfiltered reviews. Notably, Reddit is one of the top-cited sources in Google’s AI Overviews, accounting for 2.2% of all citations—more than any other single domain . This makes a presence there doubly valuable.
Quora & Niche Forums
Quora is a question-and-answer platform where users can tap into the knowledge of experts and enthusiasts. Answering questions related to your industry on Quora can establish your brand as a helpful authority. Similarly, for almost every industry or hobby, there is a dedicated online forum. Participating authentically in these communities can build trust and drive highly qualified, high-intent traffic.
Top Citation Sources in AI Overviews
| Source | Percentage of AI Overview Citations |
| 2.2% | |
| YouTube | 1.9% |
| Quora | 1.5% |
Success in this ecosystem requires a shift from broadcasting to participating by adding value to conversations, not just advertising. By understanding and optimising for each of these four quadrants, businesses can build a truly resilient and effective Search Everywhere strategy.
The Overlap: Where Search Engine Algorithms & AI Intersect
A common misconception in the current discourse is to view traditional search engine algorithms and new generative AI models as separate, competing technologies.
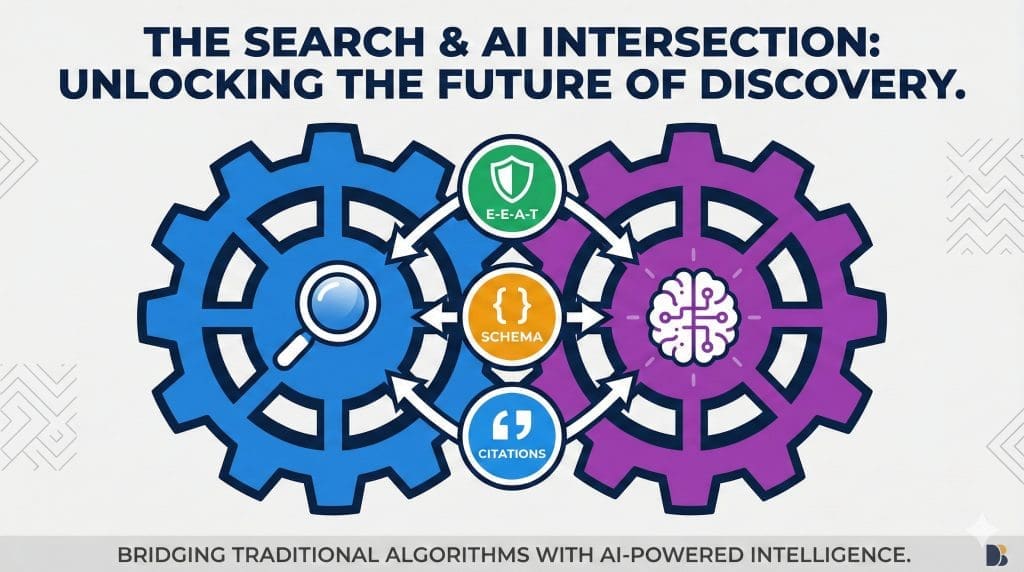
Where search and AI overlap
In reality, they are deeply intertwined. The signals that Google has been prioritising for years to improve its classic search results, including signals for quality, authority, and trustworthiness, are the very same signals that new AI models are being trained to look for when they decide which sources to cite and amplify.
The Pre-Generative Era: AI for Ranking & Interpretation (2013-2022)
For nearly a decade, Google leveraged increasingly sophisticated AI systems to refine its traditional search results. These technologies were designed to understand the nuance of human language and improve the relevance of the “ten blue links.”
| Year | Google AI System | Primary Function | Impact on SEO |
| 2013 | Hummingbird | Moved beyond keywords to understand the meaning (semantic intent) of a query. | Marked the beginning of semantic search; keyword stuffing became less effective. |
| 2015 | RankBrain | A deep learning system to interpret ambiguous or novel queries and relate them to broader concepts. | Became the third most important ranking factor; rewarded content that satisfied user intent. |
| 2018 | Neural Matching | Introduced to understand fuzzier concepts in queries and pages. | Moved beyond simple keyword matching to connect search intent with relevant content. |
| 2019 | BERT | A major breakthrough in understanding the context of words within a sentence. | Made search more conversational; rewarded natural language content. |
| 2021 | MUM | Enabled understanding of information across different formats (text, images, video) and languages. | Signalled the move towards multimodal search and content. |
| 2022-2024 | Helpful Content Updates | AI systems designed to reward people-first content while filtering out low-quality, SEO-first content. | Reinforced the importance of E-E-A-T and genuine value creation. |
These systems were all designed to help Google better understand and rank content. They taught the algorithm to value meaning over keywords and to reward content that demonstrated true expertise. This laid the perfect foundation for the generative era.
E-E-A-T as the Foundation for Both Algorithm & AI Trust
While not a direct “ranking factor” in a technical sense, it is a model that encapsulates the signals Google uses to identify high-quality, reliable content. It is also the single most important factor in becoming a citable source for AI.
Understanding E-E-A-T
| Component | Definition | How to Demonstrate |
| Experience | Does the content creator have first-hand, real-world experience with the topic? | Include personal anecdotes, case studies, original photos/videos, and evidence of direct involvement. |
| Expertise | Does the content creator have the necessary knowledge and skill in the topic? | Display credentials, qualifications, author bios, and demonstrate deep subject-matter knowledge. |
| Authoritativeness | Is the content creator or website a recognised authority on the topic? | Build a reputation through industry recognition, awards, citations from other authoritative sources, and a strong backlink profile. |
| Trustworthiness | Is the content accurate, honest, and reliable? | Cite sources, provide clear contact information, have a secure website (HTTPS), and maintain a positive online reputation. |
The E-E-A-T and AI Citation Connection
AI models are explicitly designed to combat misinformation and “hallucinations.” They do this by prioritising sources that demonstrate strong E-E-A-T signals.
Data shows that content with clear, verifiable expertise signals is 4.2 times more likely to be cited by AI systems . This is because AI models are trained to identify and surface trustworthy information.
The signals of E-E-A-T including author credentials and citations are the very signals that AI uses to determine trust.
How Structured Data (Schema) Feeds Both Search & AI Models
Structured data, implemented via Schema.org markup, is the practice of adding code to your website to explicitly tell search engines what your content is about. It translates human language into a machine-readable format.
The Role of Schema in Traditional SEO
Schema markup can lead to the generation of “rich snippets” in the SERPs (e.g., star ratings, prices, event dates), which can significantly improve click-through rates. It helps Google understand the context and relationships between entities on your page.
The Role of Schema in AI SEO
Schema is a direct line of communication to AI models. It allows you to spoon-feed them precise information about your products, services, organisation, and content. By clearly defining entities and their attributes, you make it incredibly easy for an AI to understand your information and use it to construct an answer. Rich schema implementation is strongly correlated with a higher likelihood of AI citation.
Key Schema Types for AI Visibility
| Schema Type | Purpose | AI Benefit |
| Organisation | Defines your brand’s digital identity. | Helps AI confidently identify and differentiate your brand. |
| Product | Details for every product (name, description, brand, SKU, price, availability, rating). | Enables AI to provide accurate product information in answers. |
| FAQPage | Marks up frequently asked questions and their answers. | Provides ready-made answers for AI systems to cite. |
| Article/NewsArticle | Provides context about publication date, author, and content type. | Helps AI assess the recency and authority of content. |
| Person | Defines authors and experts associated with your content. | Supports E-E-A-T signals by linking content to credible individuals. |
| HowTo | Marks up step-by-step instructions. | Provides structured, extractable content for instructional queries. |
Backlinks have been a cornerstone of SEO since its inception. They act as votes of confidence from one website to another. In the AI era, this concept of third-party validation is more important than ever, but it has expanded beyond simple links.
The Expanded Web of Trust
AI models look for a broader “web of trust.” This includes not only traditional backlinks but also:
- Citations: Mentions of your brand, people, or research on other reputable websites, even without a link.
- Entity Consistency: Consistent information about your brand (name, address, phone number, etc.) across the web.
- Presence in Authoritative Datasets: Inclusion in trusted sources like Wikipedia, industry directories, and academic papers.
The Data on Rankings & AI Citations
There is a direct and measurable link between traditional rankings and AI visibility.
Data shows that 76% of all citations in Google’s AI Overviews come from pages that already rank in the top 10 organic results. This demonstrates that strong SEO performance makes a page eligible for consideration by generative models., meaning you cannot skip the fundamentals.
The path to success in this new digital world is not to abandon the principles of good SEO, but to double down on them. The work done to build topical authority, demonstrate E-E-A-T, and structure data for machine readability pays dividends in both traditional rankings and AI visibility.
SEO 2.0: The Integrated SEO & Organic Marketing Framework
The old, linear approach of optimising a webpage and building links in a silo is no longer sufficient. Success in 2026 demands a holistic, integrated, and continuous approach.

4 pillars of SEO delivery
Our SEO 2.0 Framework is a model to help build a resilient and authoritative omni-channel brand presence.
As can be seen below, is not a linear checklist but a continuous improvement loop. It is built upon a solid Strategic Foundation and the unwavering principles of E-E-A-T, and it operates through four interconnected execution pillars: Research, Technical, Content, and Authority.

Our SEO 2.0 Framework – view the full PDF here
The Strategic Foundation Layer
Before any optimisation can begin, a solid strategic foundation must be in place.
This is the bedrock upon which the entire framework rests, ensuring that all SEO and marketing efforts are aligned with core business objectives.
- Business Vision, Goals & Knowledge: What is the ultimate goal of the business? What is its unique value proposition? What internal knowledge and data can be leveraged?
- Business Intelligence (BI): Who are the customers? What are their pain points? What are the market trends and competitive landscape?
- Marketing Strategy: How does search fit into the broader marketing mix? What is the overall brand message and positioning?
- Information Architecture (IA): How is the website and its content structured to meet user needs and facilitate intuitive navigation?
- User Experience (UX) & Design: Is the website designed to provide a seamless, engaging, and effective experience for the user on any device?
Without this foundational alignment, any SEO effort is simply a shot in the dark. The SEO 2.0 framework insists that search strategy must be derived from and fully integrated with business strategy.
The E-E-A-T Prerequisite
Layered on top of the strategic foundation is the non-negotiable bedrock of Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T). As established in the previous section, E-E-A-T is the common thread that runs through both traditional search algorithms and modern AI models. It is the universal language of credibility on the web.
Every tactic and strategy executed within the four pillars of the framework must be viewed through the lens of E-E-A-T, e.g. Does this content demonstrate real-world experience? Is it written by a credible expert? Does it build our brand’s authority? Does it enhance user trust? If the answer to any of these questions is no, the tactic should be reconsidered.
In our SEO 2.0 model, E-E-A-T must be prerequisite for every action.
The Four Pillars of SEO 2.0
The next layer is for delivery where we have four interconnected pillars that form a continuous cycle of research, technical implementation, content creation, and authority amplification.
The key is integration where no pillar operates in isolation. Insights from research inform the technical foundation, which enables the content to perform, which is then amplified to build authority, which in turn provides new data for research.
Pillar 1: Omni-Channel Research
Effective strategy begins with deep understanding and the research pillar is about gathering intelligence from across the entire omni-channel ecosystem to inform every subsequent action. It moves beyond traditional keyword research to build a comprehensive picture of the market, competitors, and customer journey.
Business & Market Analysis
This foundational step involves using Business Intelligence (BI) tools and market research to understand the total addressable market, key customer segments, and emerging trends. It answers the question: “Where are the business opportunities?” This includes analysing internal sales data, customer feedback, and industry reports to identify the most valuable areas to focus SEO efforts.
Competitor & AI Citation Research
This involves two distinct activities. First, traditional competitor analysis to see who ranks for key terms on Google. Second, and more importantly, it involves AI Citation Research: using tools and manual queries to identify which competitors and sources are being cited by AI Answer Engines like ChatGPT and Google’s AI Overviews for your most important topics.
This answers the question: “Who is winning the authority game right now?”
How to Conduct AI Citation Research:
| Step | Action |
| 1 | Identify your top 20-50 most important keywords and topics. |
| 2 | Query each topic in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google (to trigger AI Overviews). |
| 3 | Document which sources are cited for each query. |
| 4 | Analyse the common characteristics of cited sources (content format, length, structure, authority signals). |
| 5 | Identify gaps where your brand is not being cited but should be. |
Persona & AI Prompt Research
This involves not only understanding your target audience’s demographics and pain points but also researching the actual language they use when interacting with AI. This includes analysing common questions, conversational queries, and the types of prompts they use in platforms like ChatGPT. This answers the question: “How does our audience ask for help?”
This is the capstone of the research phase. It involves synthesising all the gathered intelligence to map out the core topics and sub-topics your brand needs to own to be seen as an authority. This plan informs the entire content strategy, ensuring that you are comprehensively covering the subject matter required to achieve integrated SEO, ensuring visibility across all search formats and platforms.
Pillar 2: Technical Foundation for Omni SEO
A sophisticated content and authority strategy is useless if the technical foundation is weak. This pillar ensures your website is perfectly optimised for both human users and the multitude of algorithms and AI crawlers that will be accessing it. The goal is to create a technically flawless foundation for Omni SEO.
Modern Site & for Users & AI
This involves creating a logical, hierarchical site structure that is easy for both users and crawlers to navigate. Key elements include a clear menu structure, logical URL patterns, and the use of hub-and-spoke models for core topics. The goal is to create a clear “information architecture” that mirrors the topical authority plan from the research phase.
Advanced Schema for AI & Search
Creating advanced schema involves implementing a comprehensive structured data strategy using Schema.org to explicitly define your brand, products, services, authors, and content for machines. This includes Organisation, Product, Service, FAQPage, Person, and HowTo schema, among others.
Crawl Budget & Index Control
This ensures that search engine and AI crawlers can efficiently find and process your most important content. It involves using tools like robots.txt and XML sitemaps to guide crawlers, ensuring that valuable “crawl budget” isn’t wasted on low-value pages like filtered product listings or duplicate content.
Core Web Vitals & Performance
Site speed and user experience are fundamental trust signals. This involves optimising for Google’s Core Web Vitals:
| Metric | Full Name | What It Measures | Target |
| LCP | Largest Contentful Paint | Loading performance | < 2.5 seconds |
| INP | Interaction to Next Paint | Interactivity | < 200 milliseconds |
| CLS | Cumulative Layout Shift | Visual stability | < 0.1 |
Pillar 3: Content for Search Everywhere Optimisation
Think of content as the fuel for SEO 2.0, well any form of marketing really.
This pillar is about creating and optimising content that is designed to perform across the entire Search Everywhere Optimisation landscape, from traditional SERPs to AI answers and social platforms.
On-Page SEO for E-E-A-T
This involves applying best practices of on-page SEO to every piece of content, but with a specific focus on signalling E-E-A-T. This includes clear author bios with credentials, citing sources and linking to authoritative studies, and showcasing real-world experience through case studies and original data.
PAA & Answer Engine Optimisation (AEO)
This is the practice of structuring content to be easily citable by AI. It involves several key techniques:
| Technique | Description |
| Answer-First Approach | Begin articles with a direct, concise summary of 40-60 words that immediately answers the primary user query. |
| Clear Headings | Use clear, descriptive H2 and H3 headings that often mirror the structure of user questions (e.g., “What is…?”, “How do you…?”). |
| Chunking | Use short paragraphs, bullet points, numbered steps, and tables to break down complex information into digestible chunks. |
| FAQPage Schema | Implement FAQPage schema to mark up questions and answers for easy extraction. |
Video Search Optimisation (YouTube SEO)
Recognising YouTube as the second-largest search engine, this involves creating a dedicated video content strategy.
Key optimisation tactics include:
- Optimising video titles, descriptions, and tags with relevant keywords.
- Creating engaging, keyword-rich thumbnails.
- Using transcripts and closed captions to make the content accessible to search crawlers.
- Encouraging engagement (likes, comments, shares) to signal quality to the algorithm.
Visual Search Optimisation (Lens & Image SEO)
This involves optimising images for discovery in Google Lens and image search. Google Lens now processes over 20 billion visual searches per month.
Key tactics include:
- Using descriptive, keyword-rich filenames (e.g. oak-fence-panel-6ft.jpg instead of IMG_1234.jpg).
- Writing comprehensive ALT text that describes the image content.
- Ensuring images are high-quality, mobile-friendly, and load quickly.
- Embedding relevant structured data (e.g. Product schema for product images).
The final pillar is about amplifying your content and building your brand’s authority across the web. In a modern Integrated SEO model, this goes far beyond traditional link building. It’s about building a web of trust and a strong brand presence wherever your audience spends their time.
Building Third-Party Citations
This means actively seeking mentions of your brand, experts, and research on other authoritative websites, even without a direct link. This can be achieved through digital PR, sponsoring research, or contributing to industry reports. The goal is to build a consistent “entity footprint” across the web.
Community Engagement (Reddit, Quora)
This involves authentically participating in relevant communities on platforms like Reddit and Quora. It’s not about spamming links, but about providing genuine value, answering questions, and establishing your brand and its people as helpful experts. Given that Reddit is the most-cited source in AI Overviews, this is a high-value activity.
This is the practice of creating newsworthy content, data, or stories and pitching them to journalists and editors at high-authority publications to earn media coverage and authoritative backlinks. This is one of the most effective ways to build both brand awareness and domain authority.
Strategic Link Building
While the nature of authority has broadened, traditional link building is still valuable. This involves a strategic and targeted approach to acquiring high-quality, relevant backlinks from respected websites within your industry. The focus should be on quality over quantity, prioritising links from sites with high topical relevance and strong E-E-A-T signals.
Case Study: An SEO 2.0 Audit
Theory is one thing, but application is what matters. This section details a real-world audit and analysis conducted for one of our clients.

Client case study – SEO 2.0 audit
For over two years we had achieved phenomenal success, helping them to reach position 1 in organic search results for national keywords with hundreds of thousands of monthly UK searches. Then came the gradual decline in rankings, clicks and sales.
This section showcases how the SEO 2.0 framework was used to diagnose the situation, identify critical gaps in their digital strategy and provide a clear, actionable roadmap for regaining their rankings.
The Challenge: Declining Visibility in a Crowded Market
The client, a well-established UK retailer was facing a troubling trend that only seemed be be impacting rankings in some cases but more so traffic and clicks across their product ranges, despite having strong brand recognition and topical authority.
What we noticed was that more agile competitors were starting to outrank them for valuable commercial keywords, dominating the rich features of the SERP, and capturing a growing share of the market.
We needed to understand why traditional SEO efforts were failing and what they needed to do to reclaim their market leadership online.
Visibility in SERP Features
Our audit began with a deep dive into the SERP for high-value keywords where we noticed three things:
- Some keywords were ranking as strong as ever, but Google Search Console was reporting a drop of 20-80% in clicks.
- Other keywords were simply declining in ranking month-by-month.
- When looking in Semrush, a few competitors appeared to be overtaking.
What we found was very revealing.
| SERP Feature | Competitor Strategy |
| AI Overviews & PAA | More visibility from “how-to” articles, installation guides, and FAQ sections. |
| Image & Video Packs | Higher quality lifestyle images, project galleries, and video content. |
| Citations | Greater mentions on local and national media/press and third-party citations. |
The three features above represented a key difference for some searches, but not all.
Organic Real Estate Collapse
For the keywords where rankings remained strong but clicks had plummeted, we discovered the problem wasn’t about position or even SERP features, not directly anyway.
It was more about what users actually see when they search.
Taking one keyword where we knew the client had always (and still) ranked very well, and by this I mean positions 1-5 for the past three years, our SERP analysis revealed a stark reality:
- The entire above-the-fold experience was now dominated by sponsored products, shopping carousels, and product grids.
- There were no organic blue links visible without scrolling. No local pack. No traditional search results where users would naturally click through to a website.
This meant that even ranking at position 2, directly behind a household brand name competitor, now delivered the same click-through rate that position 6–10 would have generated just a few years ago.
In this instance, the client hadn’t lost their ranking. Instead, they had lost access to the clicks that ranking used to provide.
The data confirmed this hypothesis. Google Search Console showed impressions remaining relatively stable, indicating the page was still being served in search results. However, clicks had collapsed by as much as 80% for head terms. Meanwhile, Google Analytics reported a smaller decline because the page continued to receive meaningful traffic from long-tail searches and other channels, queries where the SERP layout was less commercially aggressive.
Two Distinct Problems, Two Different Solutions
This analysis revealed that the client was actually facing two separate challenges:
|
Problem Type
|
Symptoms
|
Root Cause
|
|---|---|---|
|
CTR Collapse
|
Strong rankings, declining clicks
|
Google’s product-heavy SERP layout pushing organic results below the fold
|
|
Ranking Decline
|
Gradual position losses month-over-month
|
Competitors investing in content, schema, and SERP feature optimisation
|
For the first problem, traditional SEO tactics like would yield diminishing returns. The client already ranked as highly as realistically possible. The solution lay in competing for the SERP features that now occupied the prime real estate, including product listings, image packs, video results, and AI-generated summaries.
For the second problem, the competitor analysis above pointed directly to gaps like richer content formats and stronger off-site authority signals. Although, in a separate report, we also found that ranking decline in some cases was also due to user-experience differences where competitors appeared more specialist in certain product ranges or were innovating with richer experiences including 3D walkthroughs, virtual showrooms and product configurators. One competitor was also far more active in driving online visibility through paid search, TV ads and physical expansion.
The key insight from the research was that the competitors gaining ground were not just selling products, but were excelling in other areas.
For example:
- Becoming an authority and expert in specific niches, with focussed messaging and navigation around core product ranges.
- Driving physical expansion (and in turn more online exposure through citations and PR).
- Investing in wider forms of marketing and advertising, including influencer and promotional campaigns (TikTiok and Instagram for example).
- Creating more innovative and interactive product experiences.
- Answering every possible user question.
Some of the above overlap with traditional SEO, but on the whole, most of the competitor gains were created through a more holistic and integrated approach to marketing as a whole.
The Strategic Roadmap
The audit culminated in a strategic roadmap, which suggested that the client move away from a narrow, ranking-focused approach to a holistic, integrated SEO 2.0 strategy.
The key recommendations were to stop thinking of their marketing teams and activities in silos and to stop thinking of the website as just an eCommerce store. Instead, our proposed strategy moved them towards becoming a precise and complete resource, with the goal of becoming the most authoritative and innovative source in their vertical, wherever users might be searching.
The full circle moment was in realising that changes in search and AI had partially contributed to the loss of rankings. However, while some competitors were clearly adopting aggressive multi-million pound growth strategies, our client could compete in smarter and more effective ways by using AI. For example:
The full circle moment was in realising that changes in search and AI had partially contributed to the loss of rankings. However, while some competitors were clearly adopting aggressive multi-million pound growth strategies, our client could compete in smarter and more effective ways by using AI.
For example, using platforms like Gemini 3 Pro to create interactive, intent-driving tools that solve user problems and capture organic traffic, such as:
- Product planning and layout apps using Augmented Reality as a placement tool for users to visualise products in their homes directly from their phone.
- Virtual product assistants for users asking questions to get instant, personalised product recommendations.
- AI-powered virtual showroom with indoor/outdoor navigation and AI generated media.
- Interactive 3D product configurators for customising sizing, styles, and colours, turning passive browsing into an active design process.
The approach, while unconventional, provided a competitive differentiator for our client to regain ground and dominance in SERPs without copying competitors. It offered a roadmap to create unique value, build deeper user engagement, and establish the client as a true innovator in their space in readiness for the next wave of search evolution.
Conclusion
The way people connect with information, discover products, and make decisions has changed for good.
The era of a single, dominant search platform is over, replaced by a fragmented, dynamic, and AI-driven ecosystem. To cling to the old rules of SEO is to choose to become obsolete. Traffic patterns have shifted, user behaviours have evolved, and the very definition of “visibility” has been rewritten.
This white paper provides a clear diagnosis of this new reality and, more importantly, a clear, actionable blueprint for navigating it. The SEO 2.0 framework is a durable, strategic model for integrated SEO and building a resilient, authoritative brand presence in an omni-channel world.
It requires a fundamental shift in thinking:
- From Search Engine Optimisation to Search Everywhere Optimisation.
- From a narrow focus on rankings to a holistic pursuit of search and discovery.
- From creating content for a single algorithm to building a brand that is trusted by all of them.
- From siloed marketing functions to a deeply integrated marketing and core business strategy.
Where once the old question was, “How do I rank #1 on Google?”, the new question should be, “How do I get discovered, everywhere?”
The principles and pillars outlined in our SEO 2.0 framework, a solid strategic foundation, upfront commitment to E-E-A-T, and the continuous, integrated cycle of Research, Technical, Content, and Authority, provide the answer for how to win in this new digital world.
Appendix A: The SEO 2.0 Glossary
This appendix provides a comprehensive reference guide to the key terminology used throughout this white paper and in the broader discourse around modern search optimisation.

SEO Glossary of Terms
As the industry changes, so does its vocabulary. Understanding these terms is essential for any marketer or business leader navigating the new search landscape.
Core SEO 2.0 Concepts
SEO 2.0
The evolution of Search Engine Optimisation from a narrow focus on ranking in Google’s organic results to a holistic, integrated strategy for achieving visibility across all discovery platforms, including AI answer engines, social media, and community forums.
Integrated SEO
The core philosophy of SEO 2.0, where search optimisation is not a siloed activity but is integrated with all facets of marketing, content, user experience, and business intelligence. It emphasises the interconnectedness of all digital marketing efforts.
Universal SEO
The overarching strategy of being present and optimised across all formats of search, including text, voice, visual, and social. It aims for comprehensive visibility regardless of how or where a user initiates a search.
Omni SEO
A term reflecting the need to apply SEO principles across all channels and platforms where discovery happens. It is synonymous with the omni-channel marketing approach applied to search.
Search Everywhere Optimisation
The practical application and execution of a Universal or Omni SEO strategy. It is the action-oriented term for optimising content and brand presence across the entire fragmented search ecosystem.
AI & Generative Search Terms
AI Overviews (AIO)
AI-generated summaries that appear at the top of Google Search results for certain queries. They synthesise information from multiple web sources to provide a direct answer. Formerly known as SGE.
SGE (Search Generative Experience)
Google’s earlier Search Labs experiment name for generative AI in Search, announced in May 2023. It has since been rebranded and evolved into AI Overviews and AI Mode.
AI Mode A more complete “AI search mode” within Google Search for handling complex, multi-part questions with follow-up capabilities. It uses a “query fan-out” technique to issue multiple searches simultaneously and synthesise the results.
GEO (Generative Engine Optimisation)
A broader strategy for ensuring visibility and favourable representation within generative AI models like Gemini, ChatGPT, and Perplexity. It focuses on making content citable and trustworthy for AI systems.
AEO (Answer Engine Optimisation)
The practice of optimising content to be the definitive answer for AI-driven search queries. It focuses on structuring content to be easily extracted and cited by AI systems.
LLMO (Large Language Model Optimisation)
The technical and content-based strategies used to ensure content is easily found, parsed, understood, and trusted by large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Gemini, and Claude.
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
A technique used by AI models to enhance their responses by retrieving relevant information from external databases or the web before generating an answer. This is how many AI search tools provide up-to-date information.
Traditional SEO and Google Terms
Google’s quality framework used by its Search Quality Raters to evaluate the quality of web content. While not a direct ranking factor, it represents the signals that Google’s algorithms are designed to reward.
SERP (Search Engine Results Page)
The page displayed by a search engine in response to a user’s query. The modern SERP is a complex, modular layout featuring various elements like AI Overviews, PAA boxes, Local Packs, and organic links.
PAA (People Also Ask)
A SERP feature that displays a list of related questions to the user’s original query. Clicking on a question reveals a short, snippet-style answer extracted from a web page.
Featured Snippet
A box at the top of the SERP that provides a direct, concise answer to a query, extracted from a single web page. It can be a paragraph, list, or table.
Local Pack
A SERP feature that displays a map and a list of three local businesses for queries with local intent.
Zero-Click Search
A search where the user gets the information they need directly from the SERP (e.g., from an AI Overview or Featured Snippet) without clicking through to any website.
Schema Markup / Structured Data
Code (using Schema.org vocabulary) added to a website to help search engines understand the content and context of a page. It can lead to rich snippets in the SERPs and improves AI citability.
Core Web Vitals (CWV)
A set of metrics defined by Google that measure the real-world user experience of a web page, focusing on loading performance (LCP), interactivity (INP), and visual stability (CLS).
Platforms & Technologies
ChatGPT
An AI chatbot developed by OpenAI, based on large language models. It has become a major alternative to traditional search engines for informational queries.
Perplexity
An AI-powered search engine that provides direct answers with rigorous citations. It is known for its focus on accuracy and is popular among researchers and professionals.
Google Gemini
Google’s family of multimodal AI models that powers its AI Overviews and AI Mode features within Google Search, as well as its standalone chatbot.
Google Lens
Google’s image recognition technology that allows users to search using their camera. It processes over 20 billion visual searches per month.
Google Business Profile (GBP)
A free tool from Google that allows businesses to manage their online presence across Google, including Search and Maps. Essential for local SEO.
Measurement and Metrics
CTR (Click-Through Rate)
The percentage of users who click on a specific link or result after seeing it. A key metric for measuring the effectiveness of search visibility.
Organic Traffic
Website traffic that comes from unpaid search engine results.
AI Citation
When an AI model (like ChatGPT or Google’s AI Overview) references or quotes a specific source in its generated response. Tracking AI citations is a key metric in GEO.
The perceived expertise of a website on a specific topic, built by creating comprehensive, high-quality content that covers all aspects of that topic. with
References
First Page Sage. (2025, December 19). Google vs ChatGPT Market Share: 2025 Report.
Demand Sage. (2025, December 2 ). 50 AI Overviews Statistics 2025.
MarTech. (2025, December 1 ). What happens when no one clicks anymore.
Mediability. (2025, December 9 ). TikTok Search Boom: 40% of Gen Z Prefer TikTok Over Google.
XPLR Media. (2025, December 4 ). Andreas Briese From Google/YouTube: Today’s Search Behavior.
Gartner. (2024, February 19 ). Gartner Predicts Search Engine Volume Will Drop 25 Percent by 2026, Due to AI Chatbots and Other Virtual Agents.
Pew Research Center. (2025, July 22 ). Google users are less likely to click on links when an AI summary appears in the results.
Pew Research Center. (2025, November 20 ). Americans’ Social Media Use 2025.
Google Blog. (2025, December 11 ). AI Mode update: Gemini 3 Flash.
Google Search Central. (2025 ). Creating helpful, reliable, people-first content.
Think with Google / BCG. (2024 ). New Consumer Decision Making Process: The 4S Behaviors.
Statista. (2025 ). Voice Search Statistics.
Google Blog. (2024 ). Google Lens: 20 billion visual searches per month.






0 Comments