Traditional SEO, once focused on ranking websites in search engine results pages (SERPs) through keyword optimisation and link building is slowly being overtaken by newer forms of search. Everything changed following the launch of ChatGPT in November 2022. As a precursor to this report, we wrote about the potential death and future of SEO in October 2023 and it has undergone various updates as the search landscape has changed. Here, we expand beyond search engines like Google and Bing and looks at the wider LLM search and AI answer ecosystem, including AI Overviews, AI Mode, answer engines, GEO, AEO, LLMO and RAG, and what it now takes to earn mentions, citations and trust across platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini and Perplexity.
AI Means The Death of SEO? Not So Fast – Let’s Look At How AI is Shaping The Future of SEO
The fundamental change we are talking about here is the shift from ranked lists of blue-links to one of synthesised, AI-generated answers that try to present themselves as a single source of the truth. For brands not cited in Google’s AI Overviews, organic click-through rates have plummeted by 65.2% year-over-year [1]. This is not a future trend; it is a present and quantifiable threat to visibility.
The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) such as Google Gemini, OpenAI’s ChatGPT, and Perplexity has created a new “answer engine” ecosystem. The central conflict is the pivot from traditional SEO to AI SEO or Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO), a new practice focused on earning citations and mentions within AI-generated responses.
This report provides a complete glossary of emerging terminology, a data-driven analysis of economic impact, an exploration of AI in search, and an actionable playbook for adapting content and technical strategies.
For a short video overview, check out our Notebook LLM overview below:
Of, for a quick visual guide, check out our infographic below.
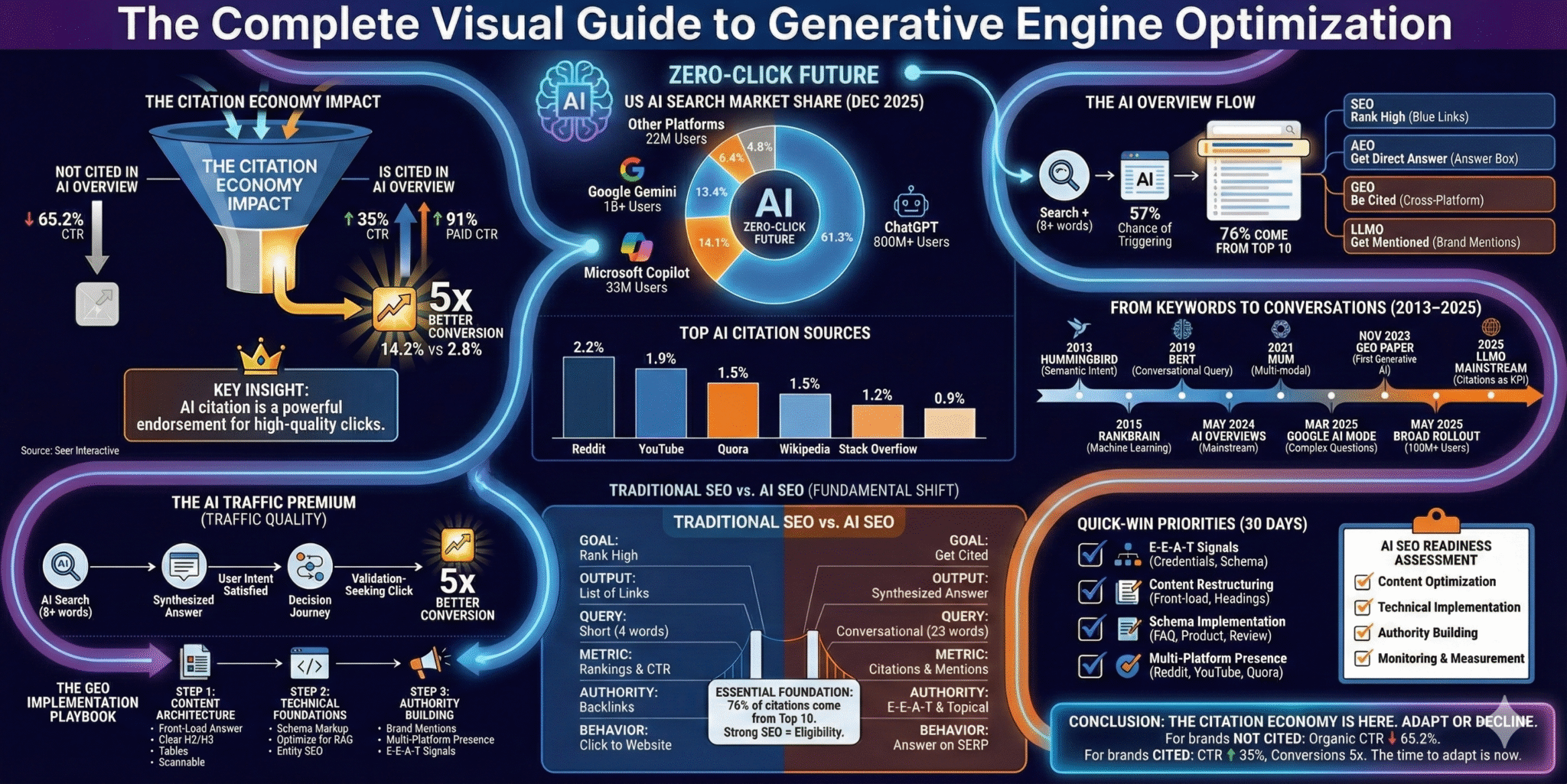
Our Complete Visual Guide to Generative Engine Optimisation infographic
Part 1: The Complete Glossary of AI SEO Terminology
- 1 Part 1: The Complete Glossary of AI SEO Terminology
- 2 Part 2: The Evolution of AI in Search
- 3 Part 3: Market Landscape & Economic Impact (Q4 2025)
- 4 Part 4: Key Distinctions and Relationships
- 5 Part 5: Strategic Framework for AI SEO Success
- 6 Part 6: The Future of AI SEO
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 References
Where once we had SEO, we now have an entire vocabulary of terms related to search optimisation, each with subtle distinctions. This glossary aims to clarify these concepts, providing a foundational understanding for anybody looking to unravel the new world of AI SEO.

AI SEO terminology: the basics
Core “Optimisation for AI Answers” Umbrella Terms
| Term | Full Name | Definition | Primary Focus | Distinction |
| AI SEO | Artificial Intelligence SEO | A broad umbrella term used in two ways: (1) Using AI to do SEO work (automation, content ideation, technical audits), and (2) Optimising to show up inside AI-driven search outputs (AI summaries, chat answers, citations). | Hybrid approach combining AI tools with AI-first optimisation | Bridges traditional and generative search optimisation |
| AEO | Answer Engine Optimisation | Optimising content to be selected as a direct answer, rather than “just” ranking as a link. Traditionally meant featured snippets, voice assistants, and answer boxes; by 2025 also includes AI summaries/answers that cite sources. | Direct answer selection and citation | Evolved from voice search and featured snippets to AI answers |
| GEO | Generative Engine Optimisation | Optimising content to improve visibility inside generative engines (systems that synthesise answers from multiple sources using LLMs). Formally introduced in an academic paper by Princeton researchers in November 2023. | Cross-platform AI citation and synthesis | Academic foundation with GEO-Bench benchmark (10,000 queries) |
| GSO | Generative Search Optimisation | A close cousin of GEO; commonly used in marketing articles to describe optimising for AI-generated search results, especially Google’s generative features and answer engines. | Practical optimisation for generative search | More marketing-focused than academic GEO framing |
| LLMO | Large Language Model Optimisation | Optimising content and brand presence so that LLM-driven products (ChatGPT Search, Google AI Mode/Overviews, Perplexity, etc.) mention, cite, or recommend you. Emphasises shifting focus from rankings/clicks to mentions/citations in conversational outputs. | LLM visibility and citation across platforms | Emphasises brand mentions beyond just citations |
| LLM SEO or LLMO | LLM-First SEO | A synonym for LLMO; optimising content so LLMs can understand, trust, and surface it in answers, often with stronger emphasis on readability, structured formatting, and being “citation-worthy.” | Content clarity and LLM comprehension | Emphasises content structure and trustworthiness |
| GAIO | Generative AI Optimisation | A broad marketing label for optimising so your brand appears in generative AI answers across platforms (not only Google). Often positioned as “next gen SEO.” | Multi-platform AI answer visibility | Platform-agnostic approach |
| AISO | AI Search Optimisation | A general term describing optimisation for AI-based search engines/experiences (chat-based search, AI summaries, AI answer engines). Frequently used as an umbrella similar to GEO/LLMO, but framed around “AI search engines” rather than “LLMs” or “generative engines.” | AI search engine visibility | Focuses on search experience rather than LLM training |
| AI Visibility | AI Search Visibility | A measurement concept: how often (and how favourably) your brand/pages appear in AI answers (citations, mentions, recommendations). Used as a practical umbrella for strategy and platform prioritisation. | Measurement and monitoring of AI presence | KPI-focused terminology |
| AI Citation Optimisation | AI Citations / Citation Readiness | Tactics aimed at increasing how often AI systems cite/link/reference your pages as supporting sources. | Earning citations from AI systems | Specific to citation-based visibility |
Google-Specific AI SERP Terms
| Term | Full Name | Definition | Launch Date | Key Characteristics |
| AI Overviews | AI Overviews (formerly SGE) | AI-generated summaries that appear inside Google Search for some queries, synthesising information from multiple sources and linking out to publishers. Evolved from Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE). | May 2024 (rollout) | Appear in ~18% of global Google searches; 30% of informational queries; 1+ billion users |
| AIO | AI Overview Optimisation | In some SEO circles, “AIO” is used to mean the feature (AI Overviews); in others it’s used to mean the practice of optimising to be cited in AI Overviews. When you see “AIO vs SEO” posts, they usually mean “optimize for being cited inside the overview, not only ranking.” | 2024+ | Dual meaning: feature + optimisation practice |
| SGE | Search Generative Experience | Google’s earlier Search Labs experiment name for generative AI in Search (announced May 2023). In common SEO shorthand, “SGE” often refers to the pre-rollout test period that led into AI Overviews. | May 2023 (experiment) | Experimental phase; predecessor to AI Overviews |
| AI Mode | AI Mode | Google’s more “end-to-end” AI Search mode (announced as a Labs experiment in March 2025, then rolled out more broadly in the US by May 2025). Uses query fan-out technique (multiple related searches across subtopics) to produce a response with links. | March 2025 (Labs); May 2025 (rollout) | 100M+ monthly active users; 6-8% session-to-external-domain conversion |
| Query Fan-Out | Query Fan-Out | Google’s description for the technique behind AI Mode: break a complex query into subtopics and issue multiple searches concurrently, then combine results into an answer with links. | 2025 | Multi-step reasoning approach |
| Deep Search | Deep Search | A deeper research mode inside AI Mode that can issue hundreds of searches and generate a “fully-cited report” style output, per Google’s I/O 2025 update. | 2025 | Extended research capability |
| Web Guide | Web Guide | A Google Search Labs experiment that uses AI (Gemini) to organise results pages into grouped categories, aiming to help exploration and discovery. | 2025 (Labs) | Clustered discovery approach |
Platform/Product Terms Influencing AI Search Optimisation
| Term | Definition | Key Characteristics | Market Position |
| ChatGPT Search | OpenAI’s built-in search experience inside ChatGPT that can search the web and return answers with links/sources, blending chat with web information. OpenAI describes it as integrating search into conversation and providing sources, plus publisher controls. | Launched October 31, 2024; 61.3% market share of AI search | Market leader in AI search |
| SearchGPT | OpenAI’s earlier prototype of AI search features (July 2024) that explicitly focused on timely answers with clear sources and publisher controls for appearance. Later fed into ChatGPT Search. | Prototype phase; emphasised publisher transparency | Predecessor to ChatGPT Search |
| Answer Engine | A generic category term for products that respond with an answer (often synthesized) rather than presenting “10 blue links” as the main outcome. Used broadly for Perplexity-like tools, AI Overviews-like SERPs, and chat search interfaces. | Describes entire product category | Emerging category |
| Conversational Search / Conversational SEO | Search behaviour and optimisation for question-like, follow-up-driven interactions rather than one-shot keyword queries. | Long-tail, multi-turn interactions | Behaviour-focused term |
| Perplexity AI | An accuracy-focused “answer engine” known for rigorous citation, making it a key target for establishing factual authority. | 22M+ monthly active users; 6.4% market share; 30% users in senior leadership | Niche but high-value platform |
| Microsoft Copilot | Microsoft’s AI-powered assistant integrated into the Bing search engine, providing direct AI-generated answers and summaries. | 33M+ active users globally; 14.1% market share | Enterprise-focused |
| Google Gemini | Powers Google’s AI Overviews and is deeply integrated with the world’s largest search engine. | 13.4% market share; 1B+ users via AI Overviews | Largest reach via Google integration |
Supporting SEO Disciplines (More Critical in AI Era)
| Term | Definition | Relevance to AI SEO | Evolution |
| Semantic SEO | Creating content around topics and meaning (entities, relationships, intent) rather than targeting single keywords in isolation. | Maps well to how LLMs interpret content; foundational for AI understanding | Older than LLM search but increasingly critical |
| Entity SEO | Optimising to be understood as a real-world entity (brand, person, product) with consistent attributes and relationships, so systems can connect you to relevant topics. | AI systems prioritise entity recognition and relationships over keywords | Gaining prominence with AI focus |
| E-E-A-T | Google’s quality framing: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness. While not “a ranking factor” in the simple sense, it’s a useful model for content and reputation signals—especially when AI systems decide what to cite. | Content with clear, verifiable expertise signals is cited 4.2x more frequently by AI systems [1] | Amplified importance with AI |
| People-First Content | Google’s official guidance focuses on content created to help people, not to manipulate rankings. | Overlaps heavily with “AI citation-worthy” content principles (clarity, usefulness, trust) | Aligned with AI priorities |
| Structured Data / Schema Optimisation | Using schema markup (FAQPage, QAPage, Product, Organisation, etc.) to make meaning machine-readable. | AirOps found schema richness correlates with higher AI citation likelihood | Critical for AI understanding |
| Information Gain | Content that adds genuinely new value (original data, distinctive analysis, first-hand experience) rather than rewriting what’s already everywhere. | Pillar for LLMO; AI systems favour novel insights | Increasingly important differentiator |
| Chunking / “Chunkable” Content | Structuring content into digestible sections (headings, lists, clear facts) that are easier for systems to extract and cite. | AirOps’ analysis heavily supports this for AI extraction | Best practice for AI readiness |
| Topical Authority | A website’s recognised expertise and comprehensive coverage of a specific subject area, signalling to search engines and answer engines that the site is a go-to resource for a topic. | 76% of AI Overview citations come from pages ranking in top 10 [1] | Critical for AI citation |
| Knowledge Graph / Knowledge Panel | Google’s system for understanding facts about entities in the world and their relationships, displayed as information boxes in SERPs. | AI systems reference knowledge graphs when generating answers | Foundational for entity understanding |
Governance, Crawling, and Licensing Terms
| Term | Definition | Status | Relevance |
| robots.txt (for AI bots) | Still a basic mechanism for controlling crawler access, though enforcement depends on bot compliance. | Established standard | Foundational control mechanism |
| llms.txt | A proposed standard (Jeremy Howard, Sept 2024) to provide LLM-friendly site guidance at inference time. | Proposed; not universally adopted | Emerging standard for LLM crawling |
| Publisher Controls for AI Search Appearance | OpenAI describes controls for publishers to manage how they appear in SearchGPT/ChatGPT Search and frames search as separate from training foundation models. | Implemented by OpenAI | Platform-specific controls |
| RSL (Really Simple Licensing) | A licensing standard aimed at letting publishers specify how AI companies can use content, positioned as building on robots.txt to block AI-powered search functions while maintaining traditional search visibility. | Proposed standard | Emerging rights management |
| Content Signals Policy | A Cloudflare initiative to express AI usage preferences (e.g., training vs other uses), reported as applying defaults across millions of domains. | Implemented | Broad-reach preference signal |
Part 2: The Evolution of AI in Search
Back in 2023, we discussed the various ways in which real-time search could factor into AI. The story now is one of continuous adaptation, driven by advancements in technology and evolving user behaviour.
AI has marked a significant inflection point, transforming SEO from a keyword-centric discipline to one focused on semantic understanding, entity recognition, and conversational interfaces.
The Pre-Generative Era: AI for Ranking and Interpretation (2013-2022)
For nearly a decade, Google leveraged increasingly sophisticated AI systems to refine its traditional search results. These technologies were designed to understand the nuance of human language and improve the relevance of the “ten blue links.”
- 2013 – Hummingbird: Google moved deeper into understanding query meaning (semantic intent) rather than pure keyword matching, marking the beginning of semantic search understanding.
- 2015 – RankBrain: As the first deep learning system deployed in Google Search, RankBrain helped the engine understand how words relate to broader concepts. Its primary function was to better rank search results for ambiguous or novel queries. RankBrain became the third most important ranking factor in Google’s algorithm [2].
- 2018 – Neural Matching: This system was introduced to understand fuzzier concepts in queries and pages, moving beyond simple keyword matching to connect search intent with relevant content.
- 2019 – BERT: A major breakthrough in natural language processing, BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) enabled Google to understand how combinations of words express different meanings and intents. It was a critical step toward comprehending conversational queries.
- 2021 – MUM (Multitask Unified Model): Introduced as an AI milestone for understanding information across formats and languages, MUM represented a significant leap in multi-modal understanding.
These systems represented major advancements, designed to perfect the existing experience by delivering a high-quality, ranked list of websites for users to explore. Their goal was to improve the library catalogue, not to write the encyclopedia itself. During this period, terms like Semantic SEO, Entity SEO, and E-E-A-T became more central because ranking systems increasingly rewarded meaning, credibility, and structured understanding.
The Answer-First Era: Featured Snippets and Voice Search (2010s-Early 2020s)
Before generative AI became mainstream, Google introduced Featured Snippets in the mid-2010s to provide direct answers on the SERP. These snippets provided concise information without requiring a click to the source website, training users to expect immediate answers. This marked the beginning of the Zero-Click Search phenomenon, where users’ queries were satisfied directly on the search results page [3].
Featured snippets became the primary source for voice search, where smart speakers like Alexa would read the snippet aloud without attribution. This early form of “answer extraction” laid the groundwork for understanding how AI systems would later synthesise information.
AEO (Answer Engine Optimisation) emerged as a practical label for optimising for featured snippets, answer boxes, and voice answers during this period. The discipline focused on:
- Clear, concise definitions (40-60 words)
- Step-by-step instructions in ordered lists
- Simple comparison tables
- Direct answers at the beginning of content
The Generative Pivot: AI for Synthesis and Answers (2023-Present)
The generative pivot marks a true architectural break. It moves AI’s role from extraction, like a Featured Snippet pulling a quote from a single source, to synthesis, where systems like AI Overviews combine information from multiple sources to generate an entirely new, comprehensive response.
- May 2023 – Search Generative Experience (SGE): Google introduced SGE as an experimental feature in Google Labs. This marked Google’s first public foray into generative AI within its primary search interface, providing AI-generated answers to complex questions directly within Google Search.
- November 2023 – GEO Academic Foundation: Six researchers from Princeton University published an academic paper titled “GEO: Generative Engine Optimization,” formally introducing the term and establishing GEO as a distinct field from SEO. The paper introduced GEO-Bench, a benchmark dataset of 10,000 queries designed to evaluate GEO techniques empirically. Results showed that certain optimization practices significantly increased the likelihood of a source being cited or included in generative engine answers, with up to 40% visibility improvement using optimization strategies [4].
- May 2024 – AI Overviews Rollout: Google officially rebranded SGE as “AI Overviews,” making it a more integrated and widely available feature within Google Search. AI Overviews now appear in approximately 18% of global Google searches and around 30% of informational queries, providing concise, AI-generated summaries at the top of the SERP [3].
- July 2024 – SearchGPT Prototype: OpenAI launched SearchGPT, a prototype of AI search features that explicitly focused on timely answers with clear sources and publisher controls for appearance.
- October 31, 2024 – ChatGPT Search Launch: OpenAI launched ChatGPT Search, replacing the SearchGPT prototype. This feature allows ChatGPT to source real-time information from the web, providing timely answers with links to relevant sources. It leverages OpenAI’s own OAI-Searchbot and partnerships with Bing Search and trusted news providers [5].
- March 2025 – AI Mode Introduction: Google introduced AI Mode as a Labs experiment, a dedicated AI-powered search experience designed to handle more complex questions with follow-ups. It uses query fan-out (multiple concurrent searches across subtopics) and is meant to be shown “as much as possible,” but can fall back to regular web results when confidence is low.
- May 2025 – AI Mode Broad Rollout: Google expanded AI Mode more broadly in the US, reporting 100 million monthly active users in the U.S. and India and that AI Overviews drive 10%+ increase in usage for query types that show them.
- 2025 – LLMO Mainstream Adoption: “LLMO” becomes a mainstream industry acronym, with guides and tooling framed around citations/mentions as primary KPIs.
The Proliferation of Terminology
The rapid rise of these generative AI platforms created a need for new terminology to describe the practice of optimising for them. While the industry has not yet reached a consensus on a single term, several have gained prominence. The reason for this proliferation is simple: search is no longer one output format.
- Traditional SEO assumed a primary output: ranked links.
- 2024-2025 mainstreamed outputs like AI Overviews, chat-based search, and AI modes that synthesise content and cite sources.
- Google explicitly describes AI Mode as combining Gemini model capabilities with Google’s “information systems” and using query fan-out to assemble responses with links.
- OpenAI’s ChatGPT Search formalises “search inside chat” with sources and publisher opportunities to be discovered.
The industry did what it always does in moments of change. It invents new labels. Some are useful. Some are basically rebranding with extra syllables. But all of them point to the same fundamental shift – the need to optimise for AI-driven answer generation rather than just traditional search rankings.
We even tried ourself back in 2023 to establish a term called GAISEO (Generative AI SEO). Thankfully, this isn’t another one to contend with among the many adopted terms today.
Part 3: Market Landscape & Economic Impact (Q4 2025)
Quantifying the shift toward AI search is the lynchpin of any successful business case for Generative Engine Optimisation. Understanding the market share of competing AI platforms and the measurable impact on user behaviour provides a clear mandate for adapting digital strategy.
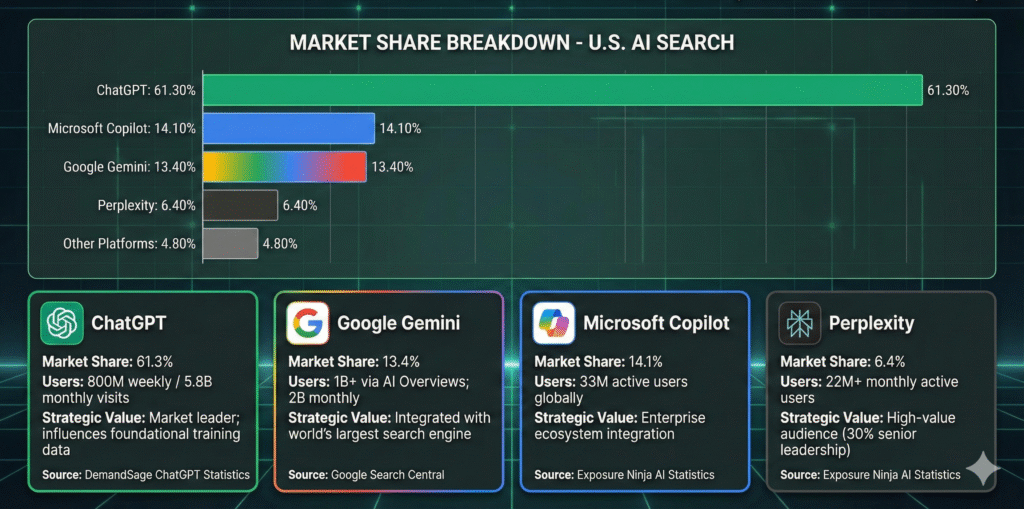
The AI search market
The Generative AI Search Market
The adoption of generative AI for information discovery has accelerated dramatically. As of Q2 2025, LLMs accounted for over 5.6% of all U.S. desktop search traffic, more than double the share from the previous year. This growth is validated by Google’s own “Year in Search 2025” report, which showed that AI tools like Gemini and DeepSeek were among the top trending global searches, confirming high user interest.
As of December 2025, the U.S. AI search market is dominated by a few key players:
| Platform | Market Share | Strategic Importance | User Base |
| ChatGPT | 61.30% | Market leader; heavily influences foundational training data and user expectations for AI answers | 800M weekly active users; 5.8B monthly visits; 81% AI chatbot market share |
| Microsoft Copilot | 14.10% | Integrated into Bing and Microsoft enterprise ecosystems; crucial for visibility in business and professional contexts | 33M active users globally |
| Google Gemini | 13.40% | Directly powers Google’s AI Overviews and is deeply integrated with the world’s largest search engine | 1B+ users via AI Overviews; 2B monthly users globally |
| Perplexity | 6.40% | Accuracy-focused “answer engine” known for rigorous citation; key target for establishing factual authority | 22M+ monthly active users; 30% in senior leadership roles |
| Other Platforms | 4.80% | Emerging players and niche platforms | Varies |
The “Zero-Click” Future and the Citation Economy
The most significant economic impact of generative search is the suppression of traditional click-through rates (CTR). A comprehensive study by Seer Interactive tracking performance through Q3 2025 revealed the stark reality of Google’s AI Overviews:
For queries with an AI Overview where a brand is NOT cited, organic CTR plummeted by a staggering 65.2% year-over-year [1]. However, for queries where a brand IS cited in the AI Overview: The brand earns a 35% higher organic CTR and a 91% higher paid CTR compared to un-cited results on the same SERP [1].
This data gives rise to the “citation economy,” a new model where the primary goal of optimisation is no longer just driving traffic but earning a direct mention, reference, or link within the AI’s synthesised answer. The 35% organic and 91% paid CTR lift for cited brands are the direct dividends paid out in this new economy. A citation acts as a powerful endorsement, driving higher-quality clicks and validating brand authority in a winner-take-all environment.
The Value of AI-Referred Traffic
While the narrative of declining clicks can seem bleak, the data reveals a powerful counter-narrative: traffic that does originate from AI search is exceptionally valuable. An analysis of over 12 million website visits found that AI search traffic converts at 5 times the rate of traditional organic traffic (14.2% vs. 2.8%) [1].
This dramatic difference is attributed to user intent. A user arriving from an AI-generated answer has already had their initial, informational queries satisfied. They are further along in their decision-making journey, more educated on the topic, and clicking through for validation or to take a specific action. This conversion premium fundamentally alters ROI calculations, justifying investment in GEO not as a traffic-driving tactic, but as a high-efficiency customer acquisition channel.
Additional Market Statistics (December 2025)
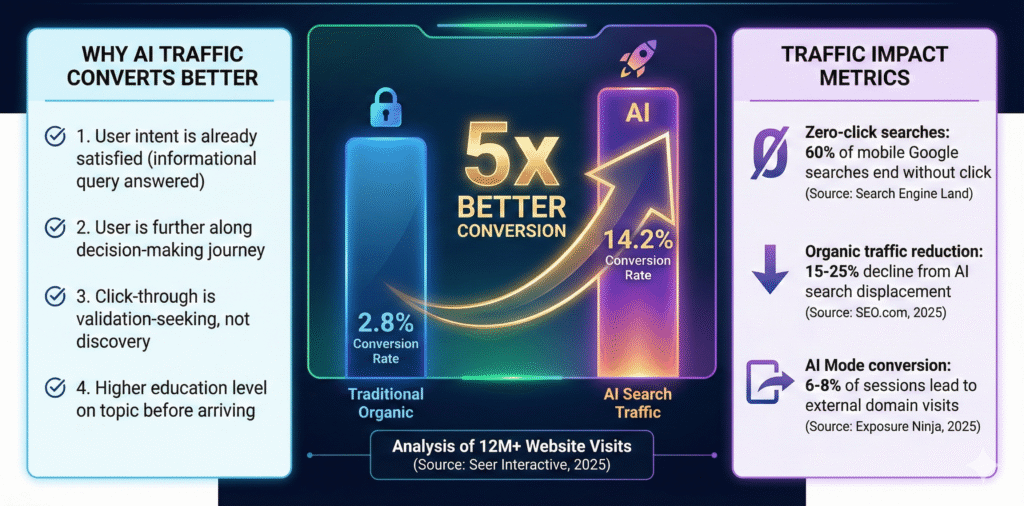
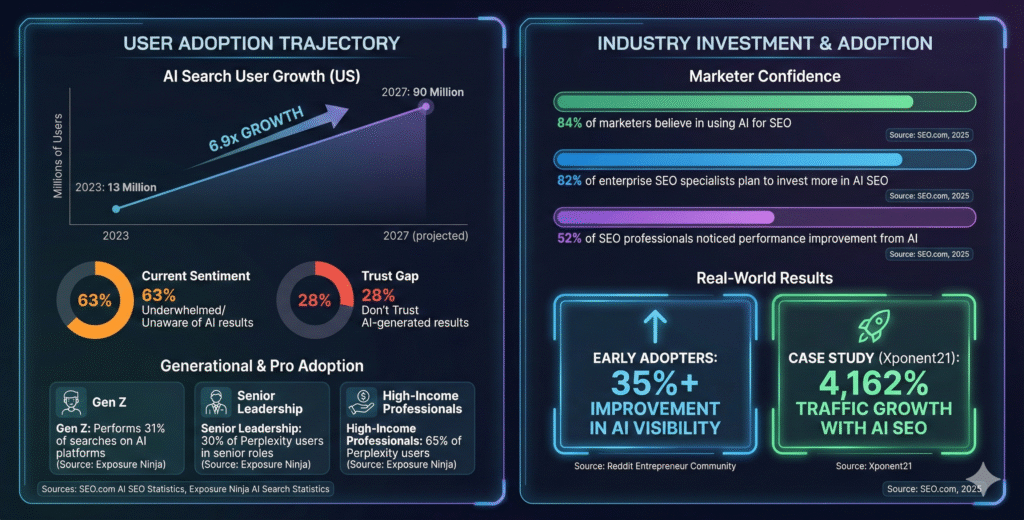
AI search traffic statistics
User Adoption and Behaviour:
- 13 million Americans used AI for search in 2023; expected to reach 90 million by 2027 [6]
- 63% of U.S. adults are underwhelmed or unaware of AI search results [6]
- 28% of U.S. adults don’t trust AI-generated search results [6]
- Gen Z performs 31% of searches on AI platforms [6]
- 60% of mobile Google searches end without a click [3]
- AI searches have reduced organic web traffic by 15-25% [6]
AI Overviews Performance:
- Appear in 18% of global Google searches [3]
- Appear in ~30% of informational queries [3]
- Queries with 8+ words have a 57% chance of triggering AI Overviews [3]
- 76% of all citations in Google’s AI Overviews come from pages that already rank in the top 10 organic results [1]
- Top citation sources: Reddit (2.2%), YouTube (1.9%), Quora (1.5%) [3]
- Drive 10%+ increase in queries for search types that show them [3]
AI SEO Adoption:
- 84% of marketers believe in using AI for SEO [6]
- 52% of SEO professionals noticed performance improvement from AI [6]
- 82% of enterprise SEO specialists plan to invest more in AI SEO [6]
- Early adopters seeing 35%+ improvement in AI visibility [7]
- Xponent21 achieved 4,162% traffic growth with AI SEO [8]
Content and AI:
- 80% of consumers rely on AI-written results for ~40% of searches [6]
- 70% of companies appreciate ChatGPT helping produce content faster [6]
- 13% of top-rated Google content is AI-generated [6]
- 19% of Google search results include AI content [6]
AI user growth and adoption
Part 4: Key Distinctions and Relationships
Traditional SEO vs. AI SEO: A Comprehensive Comparison
The fundamental shift from traditional SEO to AI SEO involves changes across multiple dimensions:
| Dimension | Traditional SEO | AI SEO (GEO/AEO/LLMO) |
| Primary Goal | Rank high in a list of blue links on a SERP | Be cited or mentioned in an AI-generated answer |
| Output Format | List of ranked results | Synthesised narrative response from multiple sources |
| Query Type | Short, keyword-focused (average 4 words) | Long, conversational, and question-based (average 23 words) |
| Content Strategy | Keyword-centric, targeting specific keywords | Answer-focused, providing comprehensive, direct answers to specific questions |
| Content Structure | Standard on-page optimisation (titles, headers, meta descriptions) | Highly structured content with clear headings, lists, tables, and schema markup |
| Technical Focus | Crawlability, site speed, mobile-friendliness, backlinks | Structured data (Schema.org), entity optimisation, RAG-friendly content |
| Authority Signals | Backlinks, domain authority, page authority | E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), topical authority, brand mentions |
| Key Metrics | Rankings, click-through rate (CTR), organic traffic, conversions | Citations, brand mentions, visibility in AI responses, quality of referred traffic |
| User Behaviour | Users click through to websites to find information | Users may get their answers directly from the AI, leading to zero-click searches |
| Citation Likelihood | N/A | Content with clear expertise signals cited 4.2x more frequently [1] |
| Traffic Quality | Standard conversion rates | AI traffic converts at 5x the rate of traditional organic traffic [1] |
The Foundation: Why Classic SEO is a Prerequisite
Generative Engine Optimisation is not a replacement for Search Engine Optimisation; it is an essential strategic layer built upon it. A successful modern search strategy recognises that traditional rankings and AI citations are deeply intertwined.
- Rankings Drive Citations: There is a direct and measurable link between traditional rankings and AI visibility. Data shows that 76% of all citations in Google’s AI Overviews come from pages that already rank in the top 10 organic results [1]. Strong SEO performance makes a page eligible for consideration by generative models.
- E-E-A-T as the Authority Signal: AI systems are designed to prioritise trustworthy sources. Content that demonstrates high levels of E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) is far more likely to be cited. In fact, content with clear, verifiable expertise signals is cited 4.2x more frequently by AI systems [1].
- A Rock-Solid Technical Foundation: The most fundamental rule remains: AI crawlers cannot cite what they cannot access efficiently. A non-negotiable technical foundation, including excellent crawlability, fast site speed (Core Web Vitals), and mobile optimisation, is the prerequisite for all other optimisation efforts.
AI Search Engine Algorithms like RankBrain vs. AI SEO: Understanding the Difference
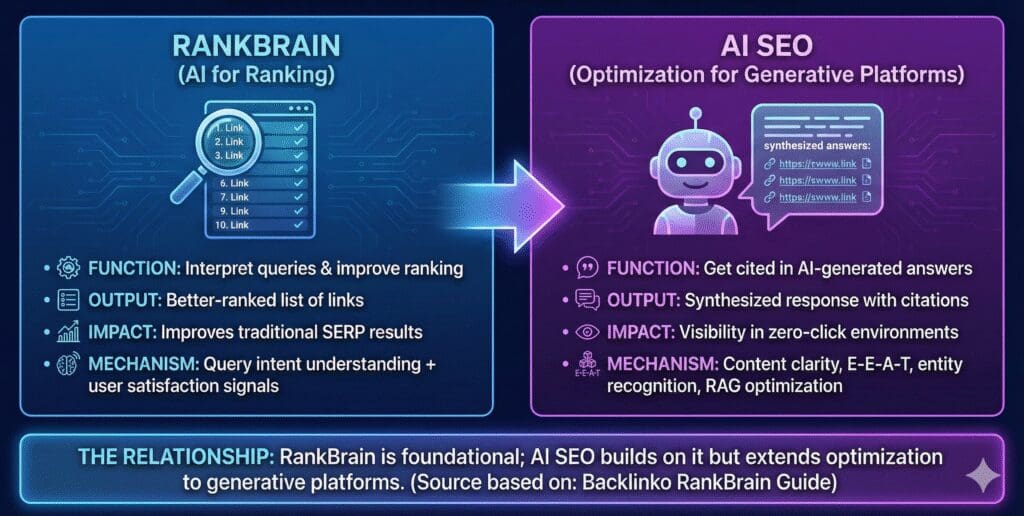
AI for ranking vs AI SEO
A lot of marketing content mixes two very different things:
- AI used inside ranking systems (RankBrain, BERT, MUM, helpful content systems)
- AI used to generate answers (AI Overviews, AI Mode)
RankBrain / BERT / MUM (AI for Understanding + Ranking)
These systems primarily:
- Interpret queries and content
- Improve relevance matching
- Help ranking systems do a better job selecting documents/features
They do not fundamentally change the output format into a synthesised response by themselves. They are “behind the scenes” technologies that improve how traditional search results are ranked and presented.
AI SEO (Optimisation for Generative Platforms)
These systems primarily:
- Focus on citation in AI-generated answers
- Optimise for platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google Gemini
- Emphasise content clarity and structure for LLM extraction
- Target conversational, longer queries
- Build topical authority and entity recognition
- Use RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) principles
- Aim for visibility in zero-click environments
The Relationship
RankBrain is foundational AI technology in traditional search. AI SEO builds on principles RankBrain uses (semantic understanding, user intent analysis) but applies them to generative platforms.
RankBrain remains important for AI SEO success because Google Gemini (which powers AI Overviews) still uses RankBrain and other ranking systems. However, optimizing for AI SEO requires additional strategies beyond traditional SEO.
Google’s AI Initiatives: SGE vs. AI Overviews vs. AI Mode vs. Web Guide
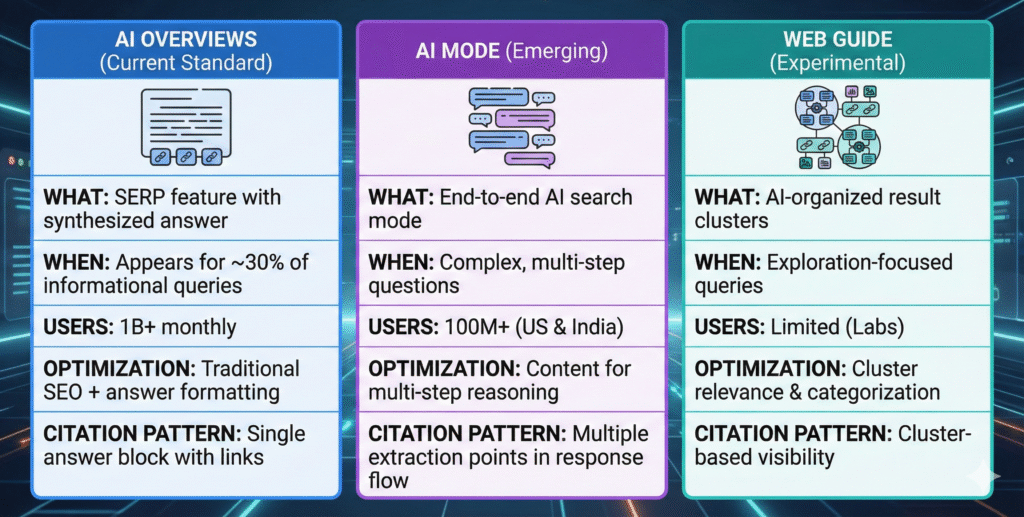
AI mode vs AI overview vs experimental features
SGE (2023) → AI Overviews (2024+): SGE was the “Search Labs” era name for Google’s generative AI experiment in Search. AI Overviews became the mainstream feature rollout name, positioned as helping people get quick understanding with links out to sources. For SEOs, “SGE optimisation” articles from 2023-early 2024 are basically early thinking about what became “AI Overviews optimisation.”
AI Overviews vs. AI Mode:
- AI Overviews: A SERP feature that appears for certain queries; it sits on top of (or within) Search results. Google says AI Overviews are used by more than a billion people (as of March 2025).
- AI Mode: A more complete “AI search mode” intended to handle more complex questions with follow-ups. It uses query fan-out (multiple concurrent searches across subtopics) and is meant to be shown “as much as possible,” but can fall back to regular web results when confidence is low.
This matters for optimisation because AI Mode can behave more like an interactive research session, meaning your content can be pulled in at different steps of the reasoning flow (comparison, constraints, trade-offs), not only “best answer paragraph.”
Web Guide: Web Guide is positioned as organised results to help exploration. That changes how “ranking” feels: visibility can become “which cluster you appear in,” not only “position 3 vs 4.”
Part 5: Strategic Framework for AI SEO Success
The GEO Implementation Playbook: A Framework for AI Visibility
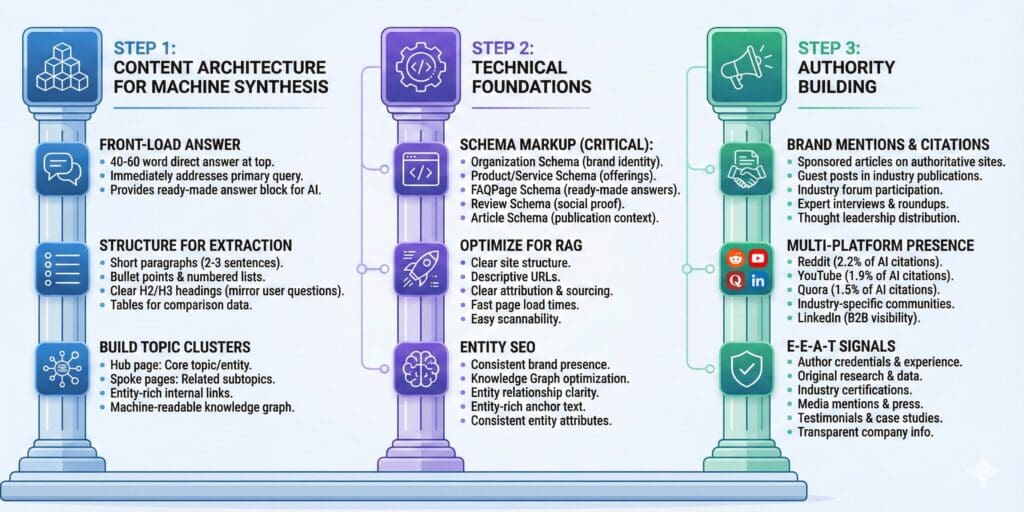
GEO implementation steps
This playbook provides an actionable, multi-faceted framework for optimising content to be understood, trusted, and ultimately cited by generative AI engines. It combines architectural content changes with rigorous technical standards and a distributed authority model
Content Architecture for Machine Synthesis
To be cited, content must be engineered for easy extraction and synthesis. The goal is to create “quote-ready” assets that AI models can parse and integrate into their responses with high confidence.
- Front-Load the Answer: Begin articles with a direct, concise summary of 40-60 words that immediately answers the primary user query. AI systems prioritize clarity and immediacy, and this format provides a ready-made answer block. This practice, known as the “answer-first” approach, is critical for AI citation.
- Structure for Extraction: Use short paragraphs, bullet points, numbered steps, and tables to break down complex information into digestible chunks. Employ clear, descriptive H2 and H3 headings that often mirror the structure of user questions (e.g., “How do you…?,” “What is…?”). This practice, known as chunking, is crucial for AI to extract and serve your content as standalone responses.
- Build Topic Clusters: Organise content around a central “hub” page for a core topic or entity, with multiple “spoke” pages covering related subtopics in exhaustive detail. Use entity-rich internal links (e.g., linking the phrase “AI search traffic conversion” instead of “click here”) to connect them and build a machine-readable knowledge graph for your domain. This approach builds topical authority, which is critical for AI citation.
Technical Foundations for LLM Visibility
Technical signals provide explicit, machine-readable context that helps AI systems categorise and trust your content. Proper implementation is a non-negotiable prerequisite for visibility.
Optimising for LLMs and AI search
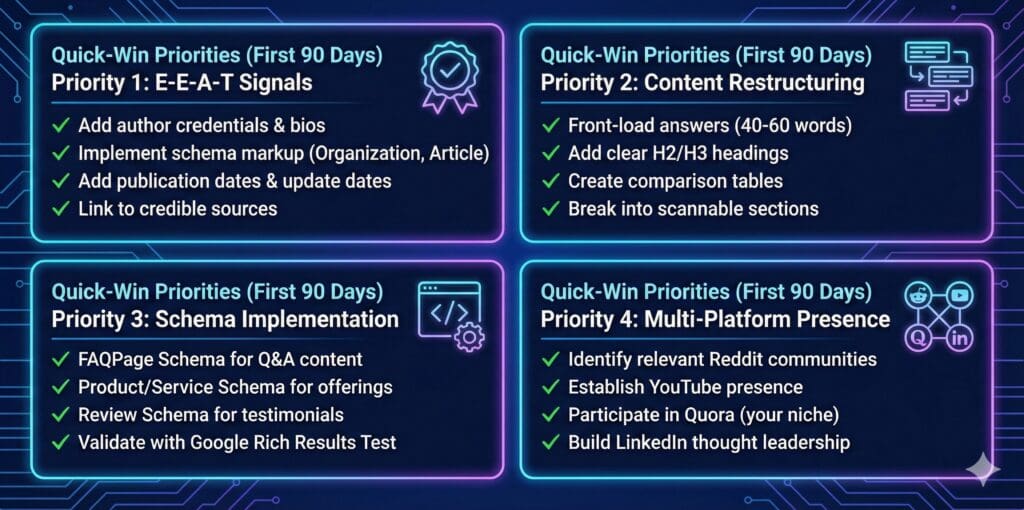
Implement Comprehensive Schema Markup
Structured data is the language that translates human content for machines. It is critical for AI visibility. Key schema types to implement include:
- Organisation Schema: Your brand’s digital identity card, helping AI confidently identify and differentiate your brand
- Product Schema: Details for every product (name, description, brand, SKU, price, availability, aggregate rating)
- Service Schema: Similar to Product Schema, defining services offered, geographic areas, and what’s included
- FAQPage Schema: Mark up frequently asked questions to provide ready-made answers for AI systems
- Review Schema: Mark up genuine customer reviews with author and rating information
- Article/NewsArticle Schema: Provides context about publication date, author, and content type
Studies show that pages with rich schema markup are cited more frequently by AI systems.
Optimise for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG is the process by which AI models retrieve external information to enhance their responses. To optimise for RAG, ensure your content is easily discoverable and citable.
This includes:
- Having a clear site structure with logical hierarchy
- Using descriptive URLs that reflect content topics
- Providing clear attribution for any data or claims
- Making content easily scannable with clear formatting
- Ensuring fast page load times for efficient retrieval
Focus on Entity SEO
Entity SEO is the practice of optimising your online presence to help AI systems understand and recognise specific entities (people, places, organisations, concepts) and their relationships.
This involves:
- Creating a consistent brand presence across the web
- Building a comprehensive Knowledge Graph for your brand
- Ensuring content clearly defines and connects relevant entities
- Using entity-rich anchor text in internal and external links
- Maintaining consistent entity attributes across all mentions
Brand mentions and citations are becoming as important as backlinks. AI models look for signals of authority and trust across the web. This means actively working to get your brand mentioned on reputable websites, in industry publications, and on social media.
Strategies include:
- Sponsored articles on authoritative sites
- Guest posts on industry publications
- Participation in industry forums and communities
- Interviews with industry experts
- Inclusion in industry roundups and “best of” lists
- Thought leadership content distribution
Build a Strong Online Presence
Beyond your own website, it’s important to have a strong presence on other platforms that AI models frequently cite, such as:
- Reddit: Highly cited in AI Overviews (2.2% of citations)
- YouTube: Second most cited platform (1.9% of citations)
- Quora: Third most cited (1.5% of citations)
- Industry-specific forums and communities
- LinkedIn for B2B visibility
- Wikipedia for brand credibility
Engaging in relevant communities and providing valuable content on these platforms can increase your brand’s visibility and authority in the eyes of AI.
Implement E-E-A-T Signals
This one isn’t new by any means, but demonstrate Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness through:
- Author bios with credentials and experience
- Published research and original data
- Industry certifications and awards
- Media mentions and press coverage
- User testimonials and case studies
- Transparent company information and team bios
- Clear, accurate, and well-sourced content
Content Strategy for AI Visibility
- Focus on Information Gain: Create content that adds genuinely new value (original data, distinctive analysis, first-hand experience) rather than rewriting what’s already everywhere. AI systems are trained to recognize and prioritise novel insights and original research.
- Create Answer-Focused Content: Instead of targeting broad keywords, focus on answering specific questions that your audience is asking. Use tools like ‘People Also Ask’ and conduct thorough keyword research to identify long-tail, conversational queries. Structure your content to provide direct, concise answers to these questions.
- Leverage Multimodal Content: Include high-quality images, videos, and other media alongside text. AI systems increasingly use multimodal understanding, and diverse content types can increase the likelihood of citation.
- Maintain Content Freshness: Regularly update content to reflect the latest information, research, and developments. AI systems favor current, accurate information.
Part 6: The Future of AI SEO
Believe it or not, AI SEO is still in its infancy, and it will continue to evolve.
As AI technology advances, we can expect to see:
- Further Integration of AI into Search: More personalised and conversational experiences will become the norm. The lines between search engines, chatbots, and personal assistants will continue to blur, creating new opportunities and challenges for marketers.
- Emergence of New Platforms: While ChatGPT, Google, and Perplexity currently dominate, new AI search platforms will likely emerge, each with its own optimisation requirements.
- Standardisation of Terminology: The industry will eventually settle on standard terminology for AI SEO practices, though this process will take time.
- Evolution of Measurement: New metrics and tools for measuring AI visibility and citation will become more sophisticated and standardised.
- Regulatory Considerations: Issues around AI training data, copyright, and publisher rights will likely lead to new regulations and standards for how AI companies can use web content.
- Increased Focus on Quality: As AI search becomes more prevalent, the importance of high-quality, authoritative, and original content will only increase.
To succeed in this dynamic environment, it is essential to:
- Stay Informed: Keep up with developments in AI search and optimisation practices
- Be Adaptable: Be willing to adjust strategies as new platforms and features emerge
- Focus on Quality: Create high-quality, user-centric content that demonstrates E-E-A-T
- Build Authority: Establish topical authority and brand recognition across multiple platforms
- Measure Strategically: Track both traditional SEO metrics and new AI-specific metrics like citations and mentions
- Integrate Holistically: Combine traditional SEO with AI SEO strategies rather than viewing them as separate disciplines
If you’re interested in using ChatGPT for SEO, make sure you check out our guide below.
Using ChatGPT For SEO: “Mind Blowing” ChatGPT SEO Guide & Case Study [UPDATED]
To learn more about the future of AI and understand the difference between AI vs AGI, our article below is a great read.
Conclusion
The evidence is overwhelming. Search has crossed a structural threshold. What began as an ecosystem of ranked links has evolved into one where answers are synthesised, condensed and increasingly presented as authoritative outputs in their own right. In this environment, visibility is no longer guaranteed by position alone. It is earned through inclusion.
Traditional SEO has not disappeared, but it has been repositioned. Rankings, crawlability, performance and links remain foundational, yet they now serve as entry requirements rather than the end goal. The decisive shift is AI-generated answers where a small number of sources are selected, cited and amplified while the rest are silently excluded. The data shows this exclusion carries real economic cost, with un-cited brands experiencing severe declines in click-through rates, and cited brands capturing disproportionate value from fewer but far higher-intent visits.
Generative Engine Optimisation is the strategic response to this shift. GEO, alongside AEO and LLMO, reframes optimisation around trust, clarity, structure and authority rather than simple discoverability. It demands content that is engineered for extraction, brands that are recognised as entities, and digital footprints that extend beyond owned websites into the wider ecosystem that AI systems learn from and reference.
This report has shown that success in AI search will come down to measurable, repeatable and grounded in well-understood principles: semantic understanding, topical depth, clear expertise signals, and robust technical foundations. Organisations that adapt early will gain the advantages, while those that wait risk becoming invisible where new generations of users increasingly make decisions.
The transition from SEO to GEO is already reshaping how information is found, trusted and acted upon. The question for brands is no longer whether to adapt, but how deliberately and how quickly they do so.\
For any readers confused about how to transition from traditional SEO to AI search, or those who prefer to use a professional SEO agency, simply get in touch to see how we can help.
If you found this report useful, or have any experiences of your own to share, please drop us a comment below or drop us a message on social media.
References
- [1] Seer Interactive. (2025). AI Overviews Impact Study: Q3 2025 Analysis
- [2] Backlinko. (2025). Google RankBrain: The Definitive Guide
- [3] Search Engine Land. (2025). A Guide to Zero-Click Searches
- [4] Wikipedia. (2025). Generative Engine Optimization
- [5] Semrush. (2025). What Is ChatGPT Search & How Does It Work?
- [6] SEO.com. (2025). 30+ AI SEO Statistics You Should Know in 2025
- [7] Reddit. (2025). Building a Company in AI Search Optimization
- [8] Xponent21. (2025). AI SEO Case Study: Xponent21’s 4,162% Traffic Growth
- [9] Conductor. (2025). How to Get Your Brand to Show Up in AI Search Results
- [10] Search Engine Journal. (2025). How To Cultivate Brand Mentions For Higher AI Search Rankings
- [11] First Page Sage. (2025). Perplexity AI Optimization: Ranking Factors and Strategy
- [12] CXL. (2025). Answer Engine Optimization (AEO): The Comprehensive Guide for 2025
- [13] HubSpot. (2025). Generative Engine Optimization: The Ultimate Guide
- [14] Neil Patel. (2025). What Is Answer Engine Optimization and Why You Need to Care
- [15] Hello, Roketto. (2025). AIO, AEO, GEO, AISO, LLMO: The Great SEO Rebrand of 2025
- [16] Google Search Central Blog. (2025). Top Ways to Ensure Your Content Performs Well in Google’s AI Experiences on Search
- [17] Microsoft Advertising Blog. (2025). Optimizing Your Content for Inclusion in AI Search Answers
- [18] Exposure Ninja. (2025). 40+ AI Search Statistics for 2025
- [19] Search Engine Land. (2025). The Origins of SEO and What They Mean for GEO and AIO




0 Comments