How to overcome a Google Penguin penalty and boost rankings with positive SEO techniques
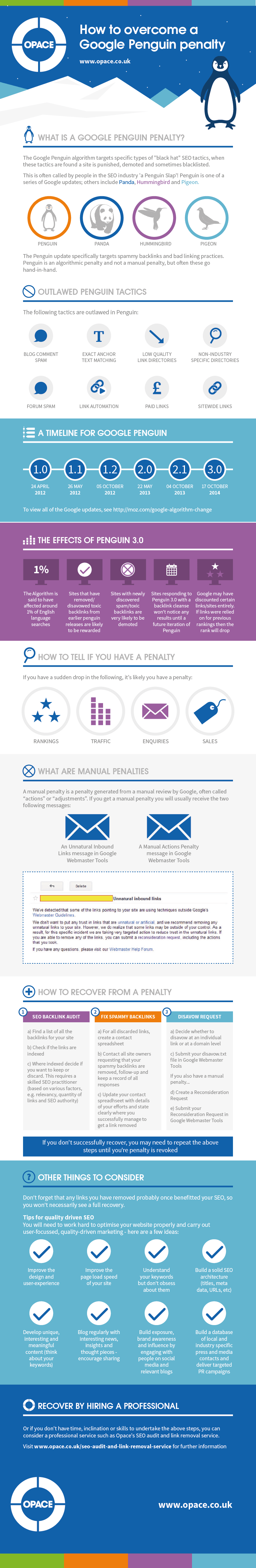
What is a Google Penguin Penalty?
The Google Penguin algorithm targets specific types of “black hat” SEO tactics, when these tactics are found a site is punished, demoted and sometimes blacklisted.
This is often called by people in the SEO industry ‘a Penguin Slap’!
Penguin is one of a series of Google updates; others include Panda, Hummingbird and Pigeon.
The Penguin update specifically targets spammy backlinks and bad linking practices.
Penguin is an algorithmic penalty and not a manual penalty, but often these go hand-in-hand.
Outlawed Penguin tactics include:
- Blog comment spam – e.g. posting comments to low quality and/or irrelevant blogs
- Exact anchor text matching – e.g. ” Lawyers London”, “Car Repairs Birmingham”
- Forum spam – e.g. adding comments/links repetitively and/or on irrelevant forums
- Link automation – using link automation software and/or private blog network methods to obtain links
- Links in low quality or non-industry specific directories – general directories or those built purely for SEO have been targeted.
- Paid links – Links which are known to have been paid for (excludes “no-follow” links) e.g. buying/selling links
- Sitewide links – These are links on every page of a site and as such classed as “unnatural”, e.g. linking to your company from every page on a blog
A timeline for Google Penguin
- Penguin 1.0 – April 24, 2012
- Penguin 1.1 – May 26, 2012
- Penguin 1.2 – October 5, 2012
- Penguin 2.0 – May 22, 2013
- Penguin 2.1 – October 4, 2013
- Penguin 3.0 – October 17, 2014 – Penguin 3.0 Still being rolled out – gradual approach.
What were the effects of Penguin 3.0?
- The Algorithm is said to have affected around 1% of English language searches
- Sites that have removed/disavowed toxic backlinks from earlier penguin releases are likely to be rewarded
- Sites with newly discovered spam/toxic backlinks are very likely to be demoted
- Sites responding to Penguin 3.0 with a backlink cleanse won’t notice any results until a future iteration of Penguin
- Google may have discounted certain links/sites entirely. If links were relied on for previous rankings then the rank will drop
How do you know if you have a penalty?
You may notice a sudden drop in rankings, traffic, enquiries or sales for previously well performing keywords.
What are manual penalties?
- A penalty generated from a manual review, often called “actions” or “adjustments”
- Usually you will receive an Unnatural Inbound Linksmessage in Google Webmaster Tools e.g.
- You will also received a Manual Actions Penaltymessage in Google Webmaster Tools e.g.
How to recover from a Google Penguin Penalty
#1 – SEO Backlink Audit
- Find a list of all the backlinks for your site
- Check if the links are indexed
- Where indexed decide if you want to keep or discard. This requires a skilled SEO practitioner (based on various factors, e.g. relevancy, quantity of links and SEO authority)
#2 – Remove Spammy Backlinks
- For all discarded links, create a contact spreadsheet
- Contact all site owners requesting that your spammy backlinks are removed, follow-up and keep a record of all responses
- Update your contact spreadsheet where site owner removes the links
#3 – Disavow Request
- For any links not removed in the above exercise, add these to a disavow file
- Decide whether to disavow at an individual link or at a domain level
- Submit your disavow.txt file in Google Webmaster Tools: https://accounts.google.com
If you also have a manual penalty…
- Create a Reconsideration Request, explaining the problem with links to any corrective work you’ve done e.g. contact spreadsheet, screenshots, Disavow file
- Submit your Reconsideration Request in Google Webmaster Tools
- Wait for a response, typically 2-4 weeks
- Repeat steps 1-3 above if unsuccessful. Google will usually provide examples of remaining spammy links
Do I need to do anything else?
Don’t forget that any links you have removed probably once benefitted your SEO, so you won’t necessarily see a full recovery. You will need to work hard to optimise your website properly and carry out user-focussed, quality-driven marketing – here are a few ideas:
- Improve the design and user-experience
- Improve the page load speed of your site
- Understand your keywords but don’t obsess about them
- Build a solid SEO architecture (titles, metadata, URLs, etc)
- Develop unique, interesting and meaningful content (think about your keywords)
- Blog regularly with interesting news, insights and thought pieces – encourage sharing
- Build exposure, brand awareness and influence by engaging with people on social media and relevant blogs
- Build a database of local and industry specific press and media contacts and deliver targeted PR campaigns
Don’t forget to audit for other penalty types e.g. Penguin.
Recover by hiring a professional service to fix your Penguin Penalty
Or if you don’t have time, inclination skills to undertake the above steps, you can consider a professional service such as Opace’s SEO audit and link removal service.
Visit /SEO-audit-and-link-removal-service/ for further information.
Follow us and share if you found this blog useful…
If you found this blog useful you can follow us below to get the latest as we release more useful internet marketing blogs over the coming months!


